Understanding Application Management | Definition & How
Application Management is a crucial element in ensuring the smooth functioning of applications, contributing to the success of the business in the long run. This article covers the details of what application management is and how can organizations include it in their business processes.
- Part 1 : What is Application Management (AM)?
- Part 2 : Application Management: AM vs ALM vs APM vs AMS
- Part 3 : Roles Involved in Application Management
- Part 4 : Types of Application Management Tools
- Part 5 : Application Management Tools Recommended
- Part 6 : Importance of Application Management
- Part 7 : Factors to Consider when Choosing Application Management Tools
- Part 8 : Best Practices for Successful Application Management
1 What is Application Management (AM)?
Application Management is a continuous set of operational processes covering the management and maintenance of software applications. It also includes the areas of troubleshooting, updates, and version control of the app.
These processes determine if the organization can handle the development and maintenance of a particular application, help produce efficient applications, and equip the business with the right tools and plans to deal with technical failures.
Application Management is a significant contributor to business owners and managers as well as the IT team. It helps them in the following ways:
- With the right set of tools and processes, business owners and managers can define a strategy to drive business growth. It is because IT application management gives them a deeper understanding of the application lifecycle processes and helps them reduce the risks of failures to a great extent.
- With the bigger picture of the application processes, the IT team can determine the right set of technologies and methodologies to enhance the operation and performance capabilities of the business.
2 Application Management: AM vs ALM vs APM vs AMS
The terms Application Management (AM), Application Lifecycle Management (ALM), Application Performance Management (APM), and Application Management Services (AMS) are closely related and some are often used interchangeably. However, they are distinct in subtle ways. Let us have an overview of each one of them. The following diagram can clearly show the relationship between AM, ALM, APM and AMS.
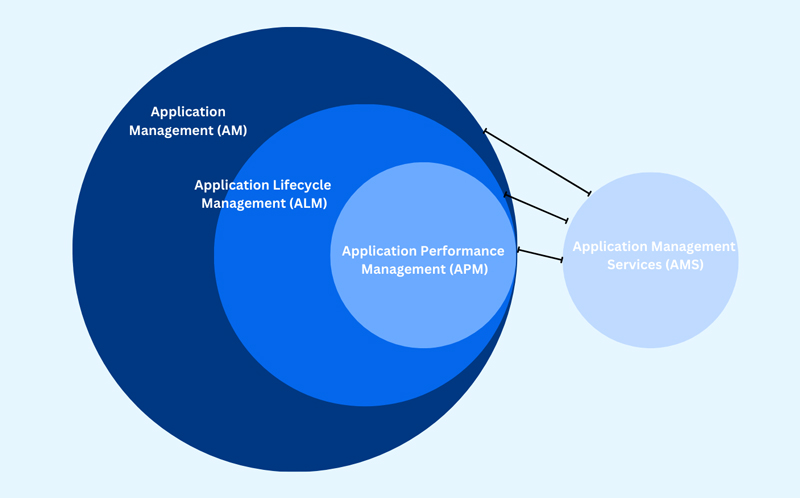
1 Application Management (AM)
Definition: Application management deals with the day-to-day management of applications including maintenance, upgradation, version control, and more.
Main Aim: The main focus of App Management is to ensure that it operates correctly on a day-to-day basis and meets the pressing, immediate requirements of the business.
Domain: It spans the operational domain, overseeing the routine operations of the apps.
Benefits: By keeping the apps up and running and ensuring consistency in their performance, AM reduces downtime and enhances productivity.
Real-World Industry Example: Shopify’s IT team uses comprehensive app management to manage several applications including those for payment gateways, plugins, inventory management, and more. They make sure all the apps for online stores are up to date and performing to their best.
2 Application Lifecycle Management (ALM)
Definition: It encompasses the whole lifecycle of an app starting from jotting down the requirements to planning, development, deployment, and operation to its retirement. In other words, it includes every phase from the app’s birth to death.
Main Aim: Overseeing all stages of an app’s lifecycle to ensure it adheres to the needs and aims of the enterprise.
Domain: It has a wider domain including planning, development, deployment, testing, maintenance, and even rolling back the apps.
Benefits: It helps ensure the usability and efficacy of apps, keeps them updated, and rolls them back when they lose utility or become a security risk.
Real-World Industry Example: JPMorgan Chase develops customized apps tailored to the needs of customers. These apps help in seamlessly carrying out mobile banking and customer banking. Thorough planning is done and testing is conducted along with regular updates to keep up with the organization’s goals of optimized customer support.
3 Application Performance Management (APM)
Definition: APM refers to monitoring and optimizing the performance of an app in real-time. It is centered around ensuring compliance with the set benchmarks of app performance in the organization.
Main Aim: The objective of Application Performance Management is to enhance user experience and to resolve performance problems as they arise so that the app keeps performing to its best.
Domain: APM is mostly concerned with enhancing user satisfaction and hence it revolves around the performance-related aspects of app management like response time, error rates, and data consumption.
Benefits: Prompt and proactive App Performance Management helps avoid and treat bottlenecks, performance glitches, optimize resource consumption, and improve user experience.
Real-World Industry Example: One of the perfect uses of APM can be found on Netflix. They are able to ensure a continuous optimized streaming experience for their users with the help of rigorous app performance management, controlling the server response time, glitches, and buffering along with upholding high standards of video quality through real-time performance monitoring.
4 App Management Services (AMS)
Definition: It refers to outsourcing the app management responsibilities to professional service providers. This can be either a third-party provider or an in-house department that takes up the entire responsibility of app management for the enterprise.
Main Aim: The objective behind hiring a specialized app management provider is to get comprehensive app management solutions that are aligned with and customized to the organization’s particular needs.
Domain: The App Management Services usually deal in all three major areas i.e. AM, ALM, and APM, thus ensuring a comprehensive solution.
Benefits: By partially or fully handing over the tedious task of app management to professionals, the organization becomes better capable of focusing on core activities while app management is also being done to its best by a qualified team.
Real-World Industry Example: Take the example of Walmart. They take services from professional app managers who oversee all the important areas like troubleshooting their online shopping apps, managing updates, and reducing downtime during high traffic periods. Handing app management over to the professional service providers helps Walmart admin focus on their core business.
The following table summarizes the focus and role of these four:
Category | App Management (AM) | Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) | Application Performance Management (APM) | Application Management Services (AMS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Day-to-day management and monitoring of the functionality. | Managing app lifecycle from conception to the rolling back of the app. | Optimization of the app’s performance. | Acquiring dedicated app management solutions. |
| Domain | Real-time, daily management, and upgradation. | From the birth of app till its rolling back, its area of operation encompasses all developmental aspects. | Resource optimization and performance analysis. | All-encompassing. Provides a comprehensive solution covering all aspects. |
| Goal | Ensuring operational excellence, and keeping the apps updated. | Adherence of app lifecycle to business goals. | Enhancing user-experience. | Getting professional support for each aspect. |
| Activities | Upgradation, version control, maintenance. | Conceiving, designing, deploying, testing, maintaining, and retiring of app. | Troubleshooting and real-time performance inspection. | Includes one or more of the three areas i.e. AP, ALM, APM. |
3 Roles Involved in Application Management
For a successful and smooth application management process, roles are assigned to different teams and individuals for clarity of responsibility. Here are some key roles involved:
1 Application Developers
A professional developers’ team is responsible for developing the apps and making sure they operate error-free.
2 Application Managers
They decide when and which new applications are needed, when an app should be updated, and when it should retire. They work in unison with the team members and guide them through the latest requirements of the organization regarding app development and management.
3 IT Management
The IT management team monitors the planning, execution, and maintenance of the app and makes sure it aligns with organizational goals.
4 IT Operations
They are responsible for day-to-day operations management for the app, performing troubleshooting, regular monitoring, and updating the app.
5 End Users
Since the app was made with the goal of enhancing user experience, end users have a huge role to play through their feedback and by pointing out the performance issues with the app. Their input helps improve the app.
6 Business Owners and Stakeholders
They are the ones who decide the goals and priorities and hence guide the app managers in planning the apps accordingly.
7 Vendor or Third Party Providers
Third-party providers, e.g., professional app management services providers give the technical support and required tools for app management. They act according to the responsibilities allocated to them, i.e., fully or partially handling the app management process.
4 Types of Application Management Tools
Let us have a look at what type of tools are needed for a robust application management process.
1 Application Performance Monitoring Tools
APM is all about gathering performance metrics by IT operations teams for the app and using them to enhance user experience. Hence, a comprehensive tool for APM should have the following capabilities:
- Real User Monitoring
- Server and Cloud Monitoring
- Network Monitoring
- Database Monitoring
- Synthetic Monitoring
2 Application Security Testing (AST) Tools
Application Security Tools are meant to provide foolproof security to the apps and cover all loopholes. An AST tool should be capable of following:
- Detecting risks
- Be able to support a variety of dynamic, static, interactive, and other types of testing techniques.
- Running automated security tests.
- Comply with security protocols.
- Cross-platform testing.
- Real-time monitoring and reporting.
3 Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) Tools
There are five main stages of ALM which are as follows:
- Requirement Gathering
- Application Development
- Application Testing
- Application Deployment
- Application Maintenance
For the Application Lifecycle, one requires tools that bring together project requirements, source code, and test management.

5 Application Management Tools Recommended
Here are some of the most commonly used, tried, and tested tools for each aspect of application management:
Application Management (AM) Tools
- Microsoft Intune: IT teams can configure, update, and secure apps across multiple devices with Microsoft Intune's app management and device security features.
- Jamf: Offers deployment, configuration, and security management for macOS and iOS apps; specializes in managing Apple devices.
Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) Tools
- Atlassian Products: The combination of Atlassian products like Jira, Confluence, and Stash can bring all the required capabilities in one place.
- Microsoft Azure DevOps Server: This ALM is a preferred choice as it utilizes the Visual Studio suite to bring together version control and configuration functionalities.
- Polarion ALM: This ALM solution by Siemens brings together people and processes by allowing secure data sharing, user permissions, and reuse of code.
Application Performance Management (APM) Tools
- Dyantrace: The tool ensures that all the computer programs are working smoothly and regularly scans them for vulnerabilities.
- Datadog APM: This tool provides you with visibility across the complete integration environment of the application from mobile and browser apps to the databases.
- AppDynamics: This APM tool by Cisco helps monitor digital applications, providing you with better access to its management.
Application Management Services (AMS) Tools
AirDroid Business: AirDroid Business Application Management is one of the most comprehensive app management solutions in the market, covering each and every aspect of app management including:
- Configuration: configure app settings and permissions seamlessly before deployment.
- Deployment: Access Google Play Store and in-house apps without user intervention.
- Security: ensure compliance with security regulations by protecting data through app policies and regulations.
- Updates: update and run apps regularly with real-time monitoring.
- Uninstalling apps: uninstall apps that need to retire.
6 Importance of Application Management
There are several benefits attached to application management, mainly because it structures the whole process and brings together all the teams in an efficient manner. Some of the benefits include:
1 Reduce Cost
When development and operations teams work together and testing exists as an integral part of the complete application development process, it helps identify bottlenecks in time. With the identification of potential risks and issues in the early stages of development, they can be fixed and save the organization from heavy costs to deal with the failures.
2 Security and Reduced Risk
Application Security processes work in parallel with all the application lifecycle processes, making it the core of the complete development process. The security engineer is not only responsible for identifying risks but also for introducing the right set of tools and infrastructure capabilities to enhance security.
3 Competitive Advantage
In the IT industry, several software ends up in failure because of improper planning and management. On the contrary, ALM is all about collecting, analyzing, and managing requirements and risks to produce a successful outcome.
4 Regulatory Compliance
With cleaner codes, effective project management, and timely risk assessments, it makes it easier to comply with the compliance requirements. The collaborative effort brings together the expertise of all the teams into the development process instead of saving them for the last minute.

Application Management Service Guide
If you want deeper insights into enterprise application management, view our PDF file. It’s loaded with detailed information to help you make the best decision for your organization's needs.
7 Factors to Consider when Choosing Application Management Tools
While selecting an application management tool, look for the following traits to make a learned decision.
1 Scalability
Choose an app that can handle the growing demands seamlessly as the number of apps, data, and users increases.
2 Synergy
Complete integration with the existing apps and devices is one of the most crucial factors to consider in a tool.
3 User-Friendliness
Look for tools with friendly and simple interfaces that offer ease of use and a comprehensive user experience.
4 Compatibility
Carefully select the app management tools that are compatible with your OS and all the devices across your IT inventory on which they would operate.
5 Cost
Take a detailed account of the costs, including the one-time costs and ongoing operational costs. Make sure the tool provides the best value for money.
6 Customization
The tool should be flexible enough to enable enough customization for workflows and reports etc. so they can offer the highest possible utility.
8 Best Practices for Successful Application Management
1 Define KPIs
You must be clear about the goals you want to attain with the app management process. Keep a record of user satisfaction rate and performance metrics.
2 Stay on Top of the Security
Make sure you carry out regular scrutiny and patch deployment to cover all vulnerabilities and keep the apps performing securely.
3 Automate Updates
To ensure you are getting the best out of your apps, they must be updated periodically. Where possible, automate this process to avoid delays and hassle.
4 Ensure Flexibility
Design and program apps keeping an eye on the future. The apps should be flexible enough to adapt to increasing amounts of data and users.
All in all, application management is an effective approach to not only execute the whole process smoothly, but also save software from potential failures and security vulnerabilities.









Leave a Reply.