Screen Mirroring Protocols: Miracast vs AirPlay vs Google Cast vs DLNA
After explaining what screen mirroring is and how it works, it's also critical to further learn about the screen mirroring protocols.
So today, we're looking at the most major screen mirroring wireless communication protocols to better understand the inner workings of screen mirroring and delving deep into each of the most popular options to see how they work.
Part 1: What Are Screen Mirroring Protocols?
Before we get into the nitty and gritty of the major screen mirroring protocols, it's important to understand what they are and why we need them.
In essence, a 'screen mirroring protocol' is a technology standard for communication between devices that enables a device to project its screen and contents to another device in real-time.
These protocols determine how the sending and receiving devices communicate and define how the data is transmitted, compressed, and displayed from your source device to the receiving display.
Besides, screen mirroring protocols also have mechanisms to help identify and connect to compatible devices in range.
Here are some key factors on why these screen mirroring protocols are important:
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Even when using devices from different manufacturers, protocols ensure interoperability.
- Advanced Codecs for Data Transmission: These protocols employ advanced codes and compression methods to ensure high-quality output.
- Wireless Convenience: Mirroring protocols simplify the pairing & connection processes without requiring an additional cables and apps.
Part 2: Common Screen Mirroring Protocols
This part introduces the common protocols for screen mirroring and its history.
DLNA

DLNA (Digital Living Network Alliance), one of the earliest released standards for sharing digital media across devices, initially released back in 2003.
DLNA is a media streaming standard that pulls media files stored on a local server to display on a TV or compatible receiving device.
Setting up a DLNA server to discover, share, and play multimedia files stored on a server created on your home network. This allows devices from different manufacturers and types of devices to communicate and share content.
However, in the day and age where streaming is normal, DLNA has significant limitations compared to newer technologies and protocols - it doesn't support live screen mirroring and requires streaming directly from a local file you manually upload to the server, rather than simply streaming it.
Miracast

Miracast, initially released back in 2012 by the Wi-Fi Alliance, is one of the most important and common screen mirroring protocols across devices and brands. Miracast was developed to be a replacement for the dreaded HDMI cable by using Wi-Fi Direct to connect devices. This made it an ideal solution for instances where people wanted to use real-time mirroring in the same LAN.
At the time, in the early 2010s is when we saw rapid adoption of wireless display technology and the Wi-Fi Alliance responded to this demand by creating a 'universal' standard that worked with devices, even across different manufacturers.
For the most part, many smart TVs, projectors, streaming devices, and Android devices support Miracast, making it one of the most accessible protocols for screen mirroring available.
But it does suffer from being a one-trick pony by only allowing full-device screen mirroring but is otherwise a capable option for native screen mirroring.
AirPlay
![]()
AirPlay is Apple's iteration of a screen mirroring protocol. It was initially introduced in 2010 with the release of iOS 4.2, which acts as a proprietary screen mirroring and media streaming protocol.
At first, 'AirPlay' was simply 'AirTunes', which was released back in 2004 to wirelessly stream audio to Apple's AirPort Express devices but as they expanded their ecosystem of devices, AirPlay evolved to support video mirroring with seamless integration across their lineup of iPhones, iPads, Macs, and Apple TVs.
And not too long ago, we also received 'AirPlay 2' in 2018 which significantly enhanced AirPlay's capabilities with improved buffering, sync, and performance and new features like multi-room audio.
Additionally, when compared to 'simpler' mirroring protocols like Miracast which only offers full-device screen mirroring, AirPlay takes things a step further by offering a more versatile approach. Instead of 'mirroring' their device to a TV, they could simply 'cast' to it to stream specific media content to compatible devices.
However, like most of Apple's products and ecosystem, AirPlay is relatively closed off compared to other screen mirroring protocols like Miracast. In recent years, we've seen a more inclusive environment for third-party TV and speaker manufacturers to support AirPlay, but it isn't as extensive as other options at its current stage which does limit the usefulness of 'AirPlay' for devices outside of Apple's ecosystem.
Google Cast

Alternatively to Apple's AirPlay, Google also has its own version, Google Cast initially introduced back in 2013. The Google Cast's main feature, however, is focused on casting specific content from apps you have on your phone or tablet to a Google/Android TV or Chromecast dongle.
This inadvertently reduces the processing load on the source device since the receiving device independently streams the content over the internet.
Over the last few years though, Google Cast has evolved and has since supported screen mirroring functionality. This is available mostly for mirroring directly Android smartphones and tablets as well as PCs using the Google Chrome web browser, including Apple's Mac lineup.
This makes Google Cast an incredibly potent tool for mirroring, considering many smart TVs and projectors these days come packed with the Android TV or Google TV operating systems.
Part 3: How Each Protocol Works
This part introduces how each screen mirroring protocol works.
DLNA
DLNA functions differently from other screen mirroring protocols as it's built on and utilizes the Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) technology which facilitates media management, device discovery and control, and content sharing across devices that are connected to the same local network via Wi-Fi or Ethernet.
This image shows you how DLNA works using UPnP:
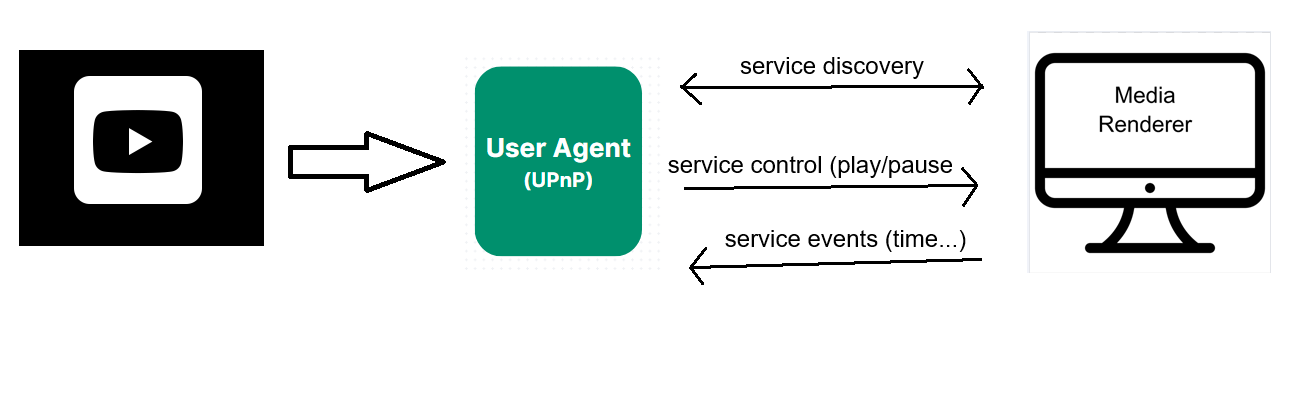
Utilizing DLNA allows multiple home network devices to store, manage, and play content stored on the server; DLNA supports a vast variety of devices, from smartphones to PCs, stereo systems, game consoles, TVs, and more.
As for the technology part, DLNA includes 4 parts:
- DMS: Digital Media Server, primarily works as a provider of media content.
- DMP: Digital Media Player, can search and play content.
- DMC: Digital Media Controller, can search and control the content played by the DMR.
- DMR: Digital Media Renderer, can renderer content provided by the DMS.
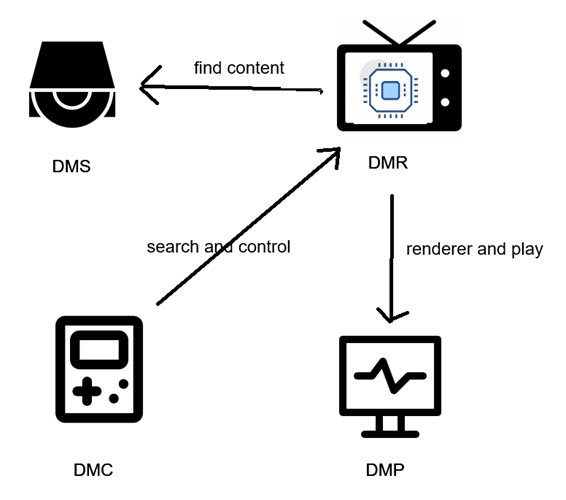
As there's a plentiful selection of methods and devices that can access DLNA servers, there isn't a specific codec it's limited to, and instead relies on the supported formats of the used devices.
But as there are only options to play stored content, this means you cannot stream from apps and services like Netflix, nor can you access screen mirroring capabilities.
Miracast
Compared to the other protocols we've mentioned so far, Miracast is sort of a 'unique' protocol in the sense that it doesn't require a local network connection to work. This is because Miracase uses the 'Wi-Fi Direct' standard (peer-to-peer), which creates its own peer-to-peer wireless connection between devices.
Using Miracast, the process is initiated and controlled via RTSP (Real-Time Streaming Protocol), and the data is transferred via RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol).
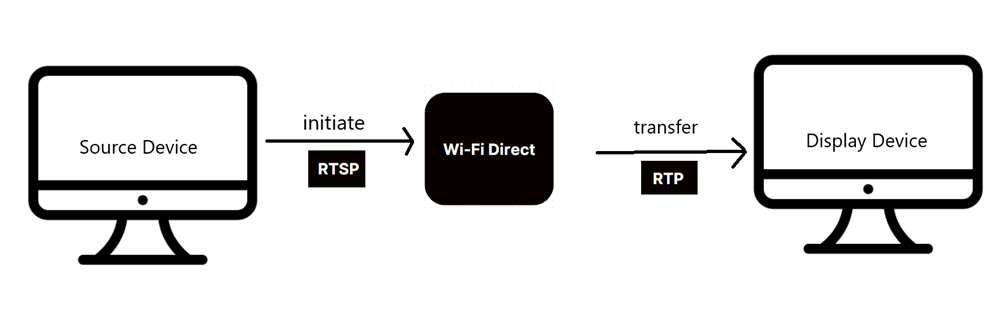
Instead of relying on both your smartphone and TV to be on the same network, Miracast's processes create a direct Wi-Fi connection between the two to enable screen mirroring. This makes Miracast an incredibly versatile tool that isn't reliant on an active and online internet connection to work.
In terms of supported codecs, for the most part, Miracast utilizes the H.264 codec to encode video and audio streams for transmission, which can reach up to 1080p HD resolutions and 5.1 surround sound.
It isn't the most 'powerful' since you can't access 4K or even 2K resolutions or take advantage of decked-out surround systems like 7.1 or 9.1 channel setups but thanks to H.264 codec support, latency is at a minimum.
And with a WPS standard, you also get WPA2 encryption which keeps your screen mirroring session safe and secure.
AirPlay
AirPlay allows both full-screen device mirroring and specified media streaming from apps. With AirPlay 2, you can also access more advanced buffering and synchronization features, such as multi-device playback to play audio on multiple AirPlay 2 compatible devices on your network.
AirPlay's standard operates over a common Wi-Fi network using proprietary protocols catered to Apple's offerings.
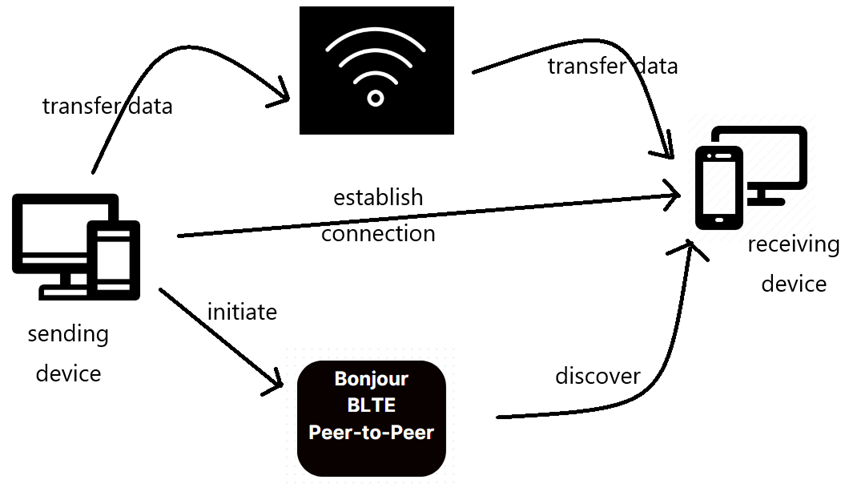
There are 3 discover methods for AirPlay:
- Bonjour: It helps Apple devices (iPhone, iPad, Mac) discover services like AirPlay and AirPrint on the same local network.
- Bluetooth Low Energy (BTLE): Apple TV broadcasts its AirPlay capabilities using Bluetooth Low Energy, which includes the IP address of the Apple TV.
- Peer-to-Peer Discovery: It allows devices (iPhone, iPad, Mac, Apple TV) to establish a direct connection without needing an existing network.
After discovering the devices, AirPlay will try to connect to the device, then encode the data, transfer the data over Wi-Fi. The receiving device will decode the data and play the content.
In terms of video quality, initially, AirPlay relied on using the H.264 format for minimal latency while retaining the quality, but ever since AirPlay 2 was introduced, they've incorporated HEVC (H.265) which has improved efficiency and quality keeping it a step ahead of other mirroring protocols.
Google Cast
In most cases, Google Cast is used to stream media content (except for some Android devices can mirror its full screen via Google Cast). There are two methods for how Google Cast works:
Method 1: via Google Cast API
This is the method how streaming services like YouTube and Netflix cast media to another screen.
First of all, the sending device sends out the content. Google Cast not only download or stream audio and video from the sender, but also loads a special lightweight webpage using HTML5, Javascript, and CSS. Then the webpage loads the content and waits for the commands such as playing, pausing, and fast forwarding.
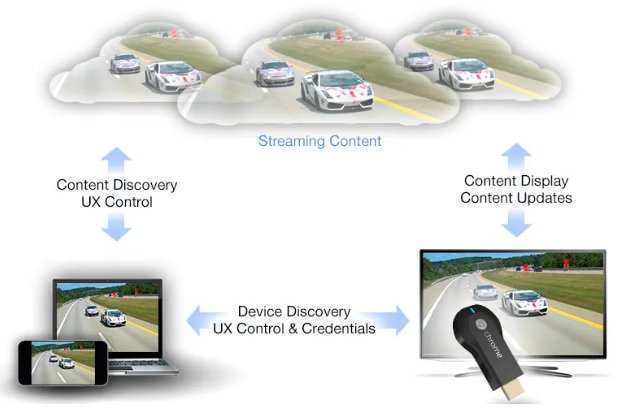
Image from Android Authority
Method 2: via Google Cast Extension
The second method doesn't need the Google Cast API. It allows you to cast the content via a Chrome web browser tab. When you use the browser tab to cast a webpage, your current page will be displayed via an HTML5 standard called WebRTC.
However, this method requires a powerful computer because your computer is continuously encoding and transmitting data.
Part 4: Differences of Screen Mirroring Protocols
This part compares the 4 screen mirroring protocols in aspects such as compatibility, connection methods, streaming quality, and more, so that they can be differentiated from each other.
| Differences | DLNA | Miracast | AirPlay | Google Cast |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Developer | Intel and Sony | Wi-Fi Alliance | Apple | |
| Compatible devices | TVs, PCs, smartphones | Android, Windows, some TVs | Apple Devices, AirPlay-enabled TVs | Android, Chrome browser, Chromecast TVs |
| Connection Method | Wi-Fi | Wi-Fi Direct | Wi-Fi | Wi-Fi |
| Security | None | WPA2 | AES Encryption | WPA2 |
| Quality | Up to 1080P | Up to 4K | Up to 4K | Up to 4K |
| Screen Mirror | × | √ | √ | √ |
| Media Streaming | √ | × | √ | √ |
Part 5: Summary
And that's everything you need to know about the major screen mirroring protocols! It can be a tad intimidating figuring out what your current devices support, but once you do you're ready to get things up and running.
The good news is many smart TVs, projectors, and monitors typically support multiple screen mirroring protocols like AirPlay and Miracast on one device. Alternatively, if you have a Google TV or Android TV, you can already access mirroring via Google Cast.









Leave a Reply.