Remote Access vs. Mobile Device Management: What's the Differences & How to Choose
In today's digital workplace, remote access and mobile device management (MDM) are crucial for ensuring business continuity and data security. However, many organizations struggle to distinguish between the two, making decision-making challenging. This article delves into their differences to assist enterprises in making informed choices.
AirDroid Business, with extensive experience in remote access and MDM, offers professional solutions and authoritative insights into these distinctions.
1 Overview of Remote Access
Definition and Principles
Remote access allows users to connect to an organization's computers, servers, or other resources via the internet without being directly connected to the internal network. This is typically achieved through technologies like Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) and Remote Desktop Protocols (RDP), which establish secure communication channels. For instance, a VPN creates an encrypted tunnel over a public network, enabling remote users to access internal resources as if they were on the organization's local network.
Application Scenarios
- Home Office: Employees working from home can connect to their office computers to access work files and use internal software. During events like the COVID-19 pandemic, many employees maintained productivity through remote access technologies.
- Business Travel: Traveling employees can access company servers anytime to retrieve the latest business data and collaborate with teams. For example, sales teams can obtain up-to-date product inventory and pricing information while visiting clients, enhancing service quality.
Advantages
- Flexibility: Employees can access organizational resources from any location with internet connectivity, breaking geographical constraints and improving work efficiency.
- Rapid Deployment: Setting up remote connections is relatively simple, allowing quick resumption of work in emergencies.
Limitations
- Limited Device Management: Focuses mainly on connection and resource access, lacking capabilities for managing the security status of employee devices or restricting application installations.
- Data Security Risks: If an employee's device is compromised, the remote access channel could endanger internal resources.
2 Overview of Mobile Device Management (MDM)
Definition and Functions
MDM is a comprehensive solution for managing mobile devices like smartphones and tablets. Its functions include device enrollment and configuration, application management (installation, uninstallation, updates), data protection (encryption, remote wipe), and security policy settings (password policies, device locking). For example, organizations can use MDM to quickly enroll employee devices and configure them according to predefined policies, such as setting up Wi-Fi connections and email accounts.
Application Scenarios
- Corporate-Owned Devices: Organizations equip employees with mobile devices and use MDM to ensure they meet security standards and business requirements. For instance, logistics companies provide customized devices to couriers, configuring them with necessary applications for order processing and logistics tracking.
- Bring Your Own Device (BYOD): Employees use personal devices for work, and MDM manages these devices securely while respecting personal privacy. Organizations can restrict the use of potentially risky applications and encrypt work-related data.
Advantages
- Robust Device Control: Comprehensively manages various aspects of devices, ensuring security and compliance while reducing data leakage risks.
- Customized Configuration: Tailors device management strategies to meet the needs of different departments and roles within the organization.
Limitations
- Higher Implementation Costs: Involves expenses for software procurement, server deployment, and personnel training.
- Employee Acceptance Challenges: Some employees may resist device management, perceiving it as an invasion of personal privacy.
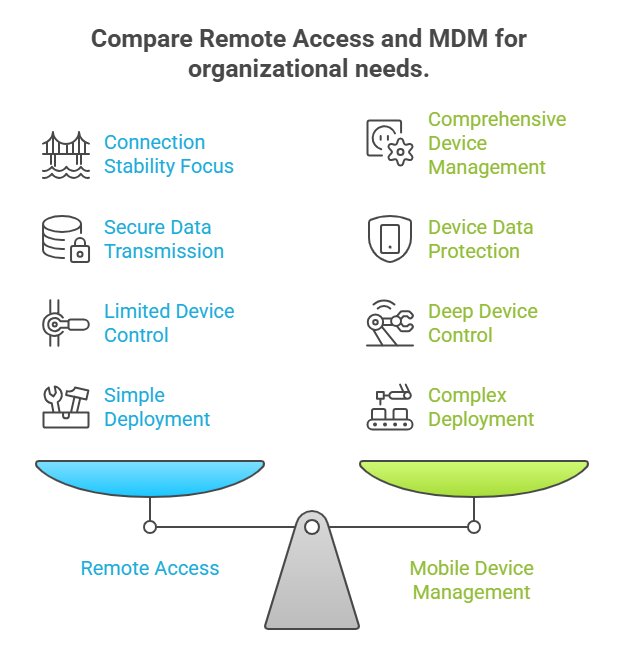
3 Comparative Analysis of Remote Access and MDM
1Management Focus Differences
Remote access emphasizes establishing secure connections between users and organizational resources, focusing on access permissions and connection stability.
In contrast, MDM focuses on comprehensive device management, covering security, application management, and data protection.
2Data Security Strategy Differences
Remote access primarily ensures the security of data transmission through encrypted connections but is weaker in managing data storage security on devices.
MDM not only secures data transmission but also protects data on devices through encryption and remote wipe capabilities.
3Control Level Differences
Remote access offers limited device control, mainly operating on connected resources without direct comprehensive device management.
MDM allows deep control over devices, such as enforcing application installations or uninstallations and setting device password policies.
4Deployment and Maintenance Cost Differences
Remote access is relatively simple to deploy, with costs mainly associated with network bandwidth and VPN software licenses; maintenance focuses on connection stability.
MDM deployment is more complex, involving software procurement, server setup, and policy configuration; maintenance requires continuous monitoring of device status and updating management policies, leading to higher costs.
4 Choosing the Right Solution for Your Organization
1Assessing Organizational Needs
Organizations should evaluate their needs based on business nature, employee work patterns, and data sensitivity. For example, creative enterprises with high work flexibility may prioritize remote access, while financial institutions handling sensitive data may require robust MDM solutions.
2Considering Budget Constraints
When selecting a solution, organizations should consider deployment costs, maintenance expenses, and software licensing fees to ensure the chosen solution fits within the budget while delivering maximum value.
3Employee Acceptance
Organizations should consider employee acceptance, especially since MDM may involve managing personal devices. Effective communication and training can help increase acceptance.
5 AirDroid Business: Integrating Advantages to Lead MDM Excellence
Integrated Functional Advantages
AirDroid Business seamlessly combines the convenience of remote access with the comprehensive management depth of MDM. It allows IT personnel to quickly connect to devices for immediate troubleshooting and operational guidance while providing end-to-end solutions for device configuration, application management, and data security.
Success Stories
- Manufacturing Enterprise: A manufacturing company uses Android devices extensively on production lines for data collection and equipment monitoring. With AirDroid Business, technicians can remotely monitor device status, quickly identify and resolve issues, and ensure only production-related applications are installed, enhancing efficiency.
- Financial Institution: A financial firm uses AirDroid Business to encrypt client information on employee devices, set strict access controls, and remotely wipe data from lost devices, effectively safeguarding client information and maintaining the organization's reputation.
Customer Service and Support
AirDroid Business offers professional customer service, including 24/7 technical support and comprehensive training resources, ensuring organizations can fully utilize the platform's features without concerns.
By understanding the differences between remote access and MDM, organizations can make informed decisions to enhance operational efficiency and data security.











Leave a Reply.