What is Remote App Management (R.A.M.)?
Remote App Management (R.A.M.) is the practice of provisioning, controlling, and securing all corporate applications used across an enterprise's entire device fleet. It utilizes a networked, centralized mechanism to achieve remote access, configuration, and full lifecycle management of applications—from employee smartphones to dedicated industrial terminals like Point-of-Sale (POS) systems and digital signage.
Remote App Management (R.A.M.) directly addresses the critical challenges faced by IT teams, such as fragmented application updates, lack of real-time control, and significant security vulnerabilities associated with deployment and data handling.
1Why is Remote App Management a Must-Have for IT?
Remote Application Management (RAM) is the foundation for secure and efficient business operations, serving as the essential solution that eliminates the chaos of manual app control. It resolves the core problem of scattered and inconsistent app updates by forcing all devices to run the current, unified software version, thereby instantly killing security gaps.
What are the Benefits of Centralized App Management?
Centralized application management systems offer substantial benefits that cater to the user's need for a standardized, unified solution:
- Boosted Efficiency: Automated deployment and updates can save IT staff hundreds of hours and significantly reduce human error.
- Enhanced Security: Ensures all devices run the latest, most secure application versions, mitigating potential data breaches. This is key to securing corporate data and privacy.
- Guaranteed Compliance: Allows for the unified pushing of compliant applications and the restriction of insecure or blacklisted app installations.
- Optimized User Experience: Provides employees with a consistent, seamless application experience, ensuring business continuity.
2Automated Strategies for Remote App Deployment?
2.1Seamless & Scalable App Deployment
To efficiently distribute applications across a large fleet of devices, modern enterprises rely on automated, scalable strategies. The most compliant and effective method for bulk install apps on Android for business is through an MDM (Mobile Device Management) solution. This is because MDM grants apps Device Owner (DO) permissions, which is the only standard and legal way to perform silent app installation on standard Android systems.
2.1.1 How to Achieve Silent App Installation using MDM (e.g., AirDroid Business)
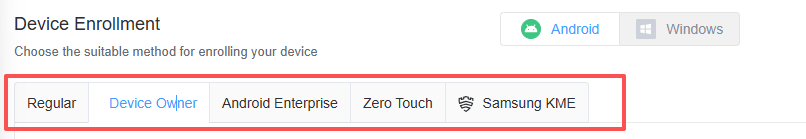
- Step 1:Device Enrollment
- Log into your MDM platform (e.g., AirDroid Business) and enroll your devices based on your deployment requirements.
To achieve Force Installation, devices typically need Device Owner (DO) privileges, though rooted devices may also be an option:
- To upload an application to Managed Google Play and then force install it, the device requires Android Enterprise / Zero-Touch / Samsung KME enrollment.
- To upload a proprietary application to the App Library and then force install it, the device needs the Device Owner (DO) enrollment method.
- If a device is enrolled using the standard method, it can only use the App Library for force installation if it is rooted.
- Step 2:Upload or Add Applications to the Library
- After enrollment, upload the applications you need to force install to the App Library or Managed Google Play. You can then publish and deploy them to the targeted devices for silent installation.
2.1.2 Importance of Force Install on Unattended Devices
Silent App Installation is a critical operational capability for unattended devices (such as digital signage, kiosks, and logistics handhelds). It allows administrators to remotely and batch-install or update critical business applications via a remote console without interrupting the device's operation or requiring any on-site action. This capability ensures all devices consistently run the latest, most secure, and unified version, significantly reducing on-site maintenance costs and downtime, which is key to boosting enterprise efficiency and ensuring business continuity.
Case Study: Digital Signage App Deployment
- 1. Problem: Digital signage dispersed across various locations requires massive manpower and causes playback interruption when the content player app needs an update.
- 2. Solution: After AE/Zero-touch enrollment, the MDM solution gains DO permission over the signage. When the content player app has an update, IT simply pushes it from the console.
- 3. Benefit: The application updates silently in the background, without interrupting the running advertisement content. This guarantees the device maintains a 24/7 continuous, high-efficiency operation and achieves zero-touch maintenance.
3How to Build a Secure Corporate App Ecosystem?
3.1Building Your Secure Corporate App Ecosystem
To ensure top-tier security and access control, enterprises must create a highly controlled application distribution environment to prevent unauthorized or malicious software installation. This is typically achieved using two main components within the MDM platform:
| Managed Google Play Store (Managed Play) | Built-in App Library (Private Store) | |
|---|---|---|
| App Source | Approved applications from the public Google Play Store. | APK files developed internally by the enterprise and not published on the Play Store. |
| Installation Method | Play Store mechanism controlled by MDM. | Direct APK upload to the MDM platform for hosting and distribution. |
| Security Advantage | Prevents employees from installing malware, with continuous scanning by Google. | Complete control over app versions and sources, preventing installation of unapproved internal test versions. |
| Silent Installation | Supported | Supported |
3.1.1 Managed Google Play Store (Corporate Google Play Store):
Managed Google Play is the core of the Android Enterprise framework, allowing businesses to create a private, controlled, and secure Google Play interface exclusively for corporate devices.
- App Whitelisting: Employees can only see and download applications explicitly approved by the administrator in the control panel.
- Malware Prevention: Automatically filters out all unsafe or unapproved public applications.
- Silent Installation & Updates: Combined with Device Owner permission, it allows for remote silent forced installation and updating of approved applications.
Setting Up Your Corporate Google Play Store:
Using AirDroid Business as an Example
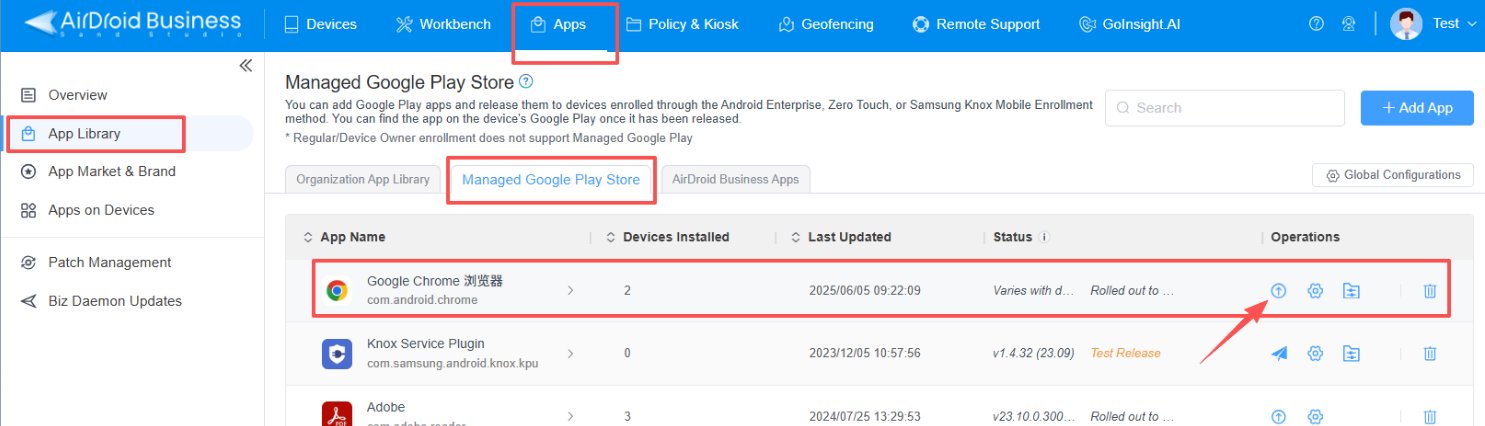
- Enroll devices into the MDM (e.g., AirDroid Business) using a method such as Android Enterprise / Zero-touch.
- Navigate to the App Library and sync with Managed Google Play to select and approve necessary public apps.
- These approved apps can then be directly force installed onto the enrolled devices.
3.1.2 Built-in App Library (Android Private App Store):
For internal, proprietary applications (private apps) that are not published on the public Play Store, the MDM platform offers an internal App Library.
- Administrators directly upload the custom APK files here for hosting and distribution.
- This gives the enterprise complete control over the application version and source, making it the best way to manage custom apps within a multi-platform integration strategy.
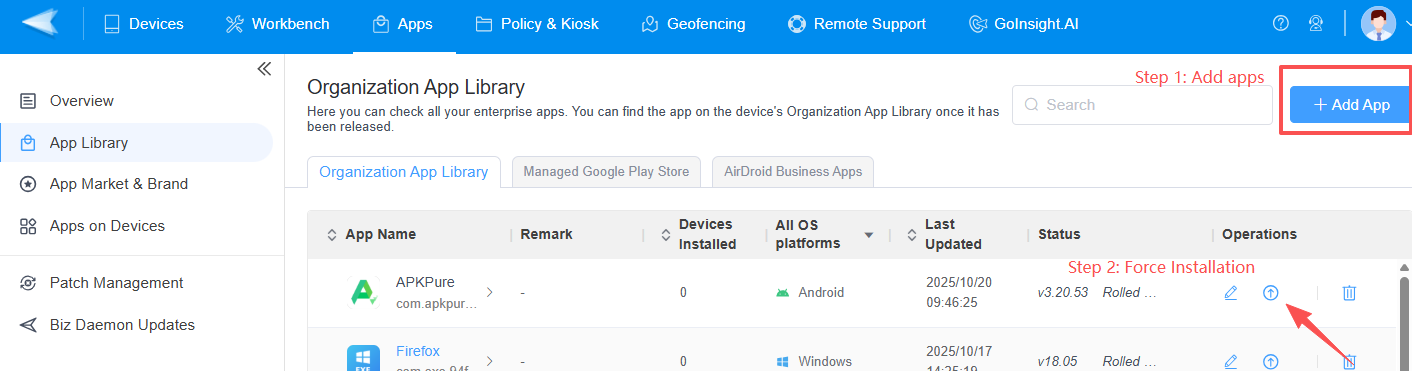
Practical Implementation (Using AirDroid Business as an Example):
- Administrators use the MDM's (e.g., AirDroid Business) App Library feature to directly upload internally developed APK files. This provides complete control over the app's source and version, ensuring employees only use tested, official enterprise applications.
3.1.3 Staged Rollout for Safer Updates:
MDM platforms support phased, non-simultaneous updates for applications from both Managed Google Play and the App Library.
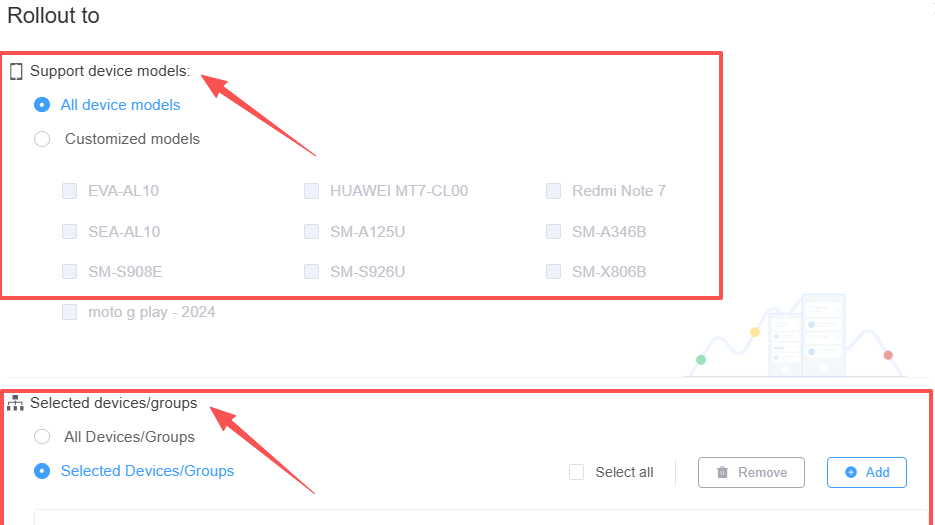
- Risk Minimization: Staged rollout minimizes risk by allowing updates to be pushed to a small "canary" group first. If issues arise, the rollout can be paused immediately, preventing mass device failure.
- Scheduling: Administrators can precisely control the scope (e.g., "by device model" or "by device group"). This is a key feature of centralized management and configuration for large device fleets.
3.2Ensuring Application Security and Data Protection
App management is fundamentally a security function, as it controls the largest threat surface on any device. R.A.M. reinforces security through:
- Risk Mitigation: The application whitelisting and private store model proactively block the installation of malicious and unauthorized software.
- Data Protection: Securing corporate apps on employee devices involves using MAM capabilities for app containerization and data isolation. In the event of device loss or employee departure, administrators can remotely wipe or isolate corporate apps and data, ensuring sensitive information remains protected.
- Vulnerability Defense: Mandatory, rapid updates ensure that all applications are promptly patched against the latest vulnerabilities, maintaining a strong defense posture.
4Special Scenarios and Operational Excellence
4.1Remote App Management in Specialized Environments
Multi-platform support and integration requires R.A.M. solutions to adapt to unique industry terminals. The core requirement in these scenarios remains: silent, remote, and non-interruptive business operation.
- Unattended and Professional Terminals: For update apps on unattended Android devices, relying on Device Owner (DO) permissions for silent forced installation is non-negotiable, ensuring core services like information display are never interrupted.
- Rugged Devices and PoS Systems:
- Control: For rugged device application management, MDM features like Kiosk Mode can lock down the terminal to run only necessary work applications, enhancing security and process uniformity.
- PoS Update Scheduling: Critical systems like Android PoS system remote app update must utilize precise application update scheduling to ensure installations occur during non-peak or overnight business hours, preventing disruptions to transaction systems.
5How to Troubleshoot Remote App Installation Failures?
Troubleshooting Remote APK Installation Failure:
Even with automation, installation failures can occur. Efficient R.A.M. solutions integrate remote application and remote desktop management tools (like remote diagnostics) to quickly resolve issues:
- Common Errors: Signature mismatches, insufficient storage space, and application permission conflicts are the most frequent causes.
- Resolution: MDM platforms provide detailed installation logs and remote diagnostic access, enabling IT staff to identify and resolve issues without needing physical access to the device. This ensures a high success rate and further supports the goal of automation and user experience improvement.
6Conclusion: The Path to Unified, Secure Remote Management
Remote App Management (R.A.M.) is the essential strategy for achieving efficient IT operations, ensuring robust information security, and maintaining business continuity in today’s distributed environment.
By implementing a comprehensive MDM solution, enterprises can successfully overcome the pain points of fragmented deployment and security risks. This approach delivers the high-level automation, centralized monitoring, and security reinforcement that IT administrators are actively seeking. The future of application deployment lies in a unified ecosystem where every application, on every device, is managed securely and seamlessly from a single control point.









Leave a Reply.