Top 5 Security Risks You Face from Unauthorized Device Tethering
The overlooked risks of unauthorized hotspot sharing
Unauthorized hotspot sharing (employees using company equipment as hotspots for external devices to access) has become a "hidden vulnerability" in enterprise network security.
This seemingly convenient workaround is far from a "minor asset usage violation," but rather a trigger that directly ignites multiple security risks—and in regulated industries, it could even threaten the survival of the enterprise, exposing organizations to an enterprise mobile security loophole.
This article will break down the five core security risks posed by unauthorized hotspot sharing, providing enterprises with risk awareness and prevention strategies.
- 1 : Risk 1: Network boundary collapse – indiscriminate access by untrusted devices
- 2 : Risk 2: Bypassing VPNs and Firewalls – Unobstructed Data Leakage Channels
- 3 : Risk 3: Direct Threat to Data Compliance – A “Match of Failure” for the Regulatory Industry
- 4 : Risk 4: Device Infection and Malware Propagation – Lateral Penetration of Enterprise Networks
- 5 : Risk 5: Network resource abuse and business service interruption – a double loss in operating costs and efficiency.
- 6 : Solution: How MDM can precisely control and block the risk of hotspot sharing
1Risk 1: Network boundary collapse – indiscriminate access by untrusted devices
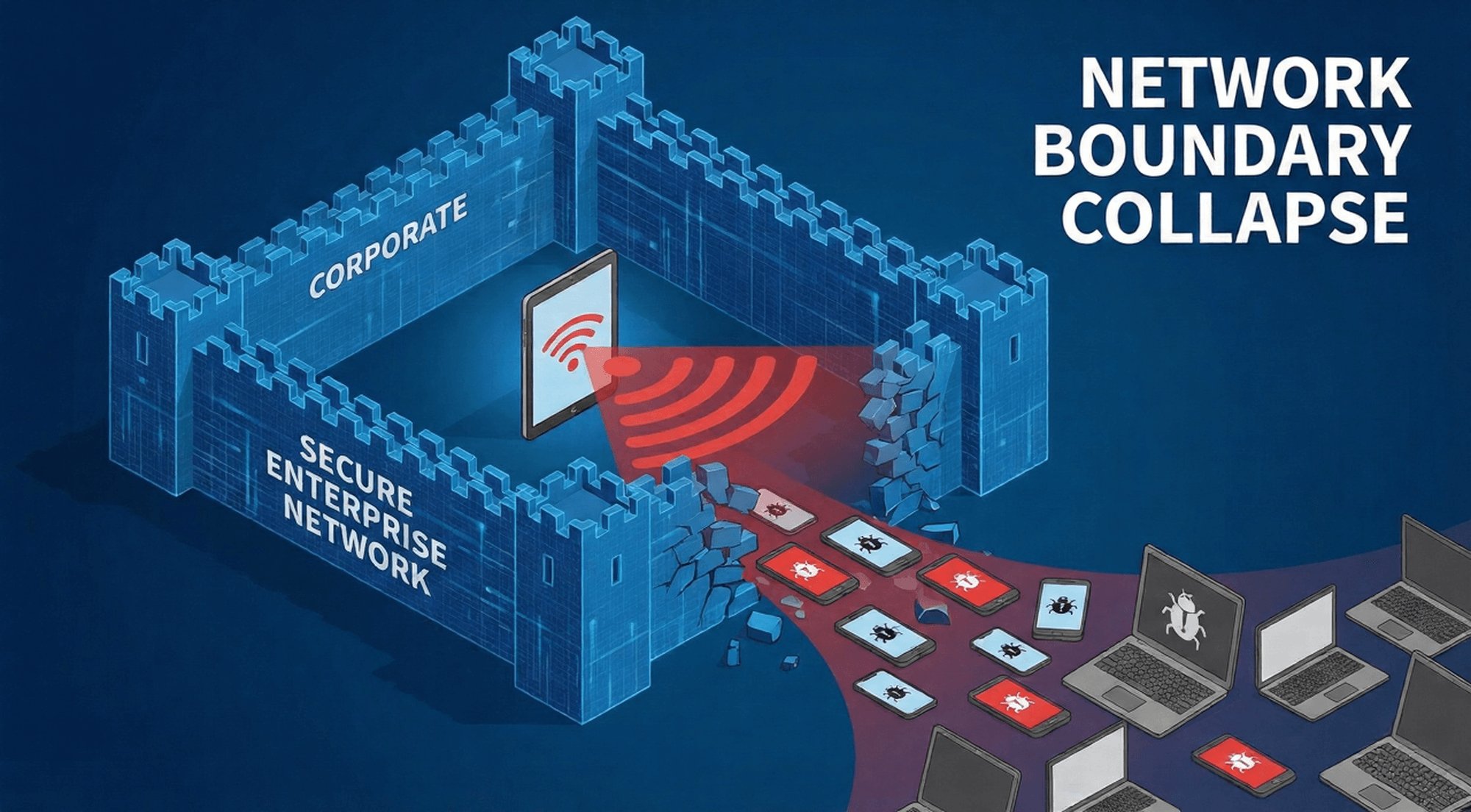
The core of enterprise network security is "clear boundaries," and unauthorized hotspot sharing directly breaches this defense, allowing untrusted external devices to freely intrude into the enterprise's controlled network of devices, resulting in unauthorized device access, amplifying the possibility of internal system compromise.
Unrestricted access to untrusted devices
Unauthorized hotspot sharing allows employees to freely connect external devices such as customer tablets, visitor phones, and personal computers to the network environment centered around enterprise equipment.
This uncontrolled connectivity leads to network perimeter defense failure, weakening the foundational security structure. These external devices have never undergone enterprise security audits: they may be "naked machines" with outdated systems and lacking antivirus software, they may be infected with malware, or they may even be "attack vectors" deliberately implanted by hackers.
Once connected, these devices gain direct connection permissions to enterprise-controlled equipment, becoming "entry points" for security threats.
Direct connection between internal network and external risks
Enterprise control devices (such as field tablets and POS terminals) are essential components of the internal security system, connecting to the enterprise intranet, sensitive data servers, or business systems.
However, hotspot sharing turns these devices into "backdoors" connecting internal and external networks: untrusted external devices can indirectly access enterprise intranet resources after connecting via hotspots, bypassing the first line of defense for physical network access (such as office area Wi-Fi authentication and server room access permissions), rendering the network boundary virtually non-existent.
This scenario undermines enterprise Wi-Fi access control, making security policies far less enforceable.
For example, an employee of a chain restaurant turned on the hotspot of the cash register (company equipment) to watch videos on their personal mobile phone. The phone was infected with a Trojan program, which directly invaded the cash register system through the hotspot connection, and then stole nearly three months of customer payment data and sales records from the store, causing direct economic losses of over 500,000 yuan.
2Risk 2: Bypassing VPNs and Firewalls – Unobstructed Data Leakage Channels
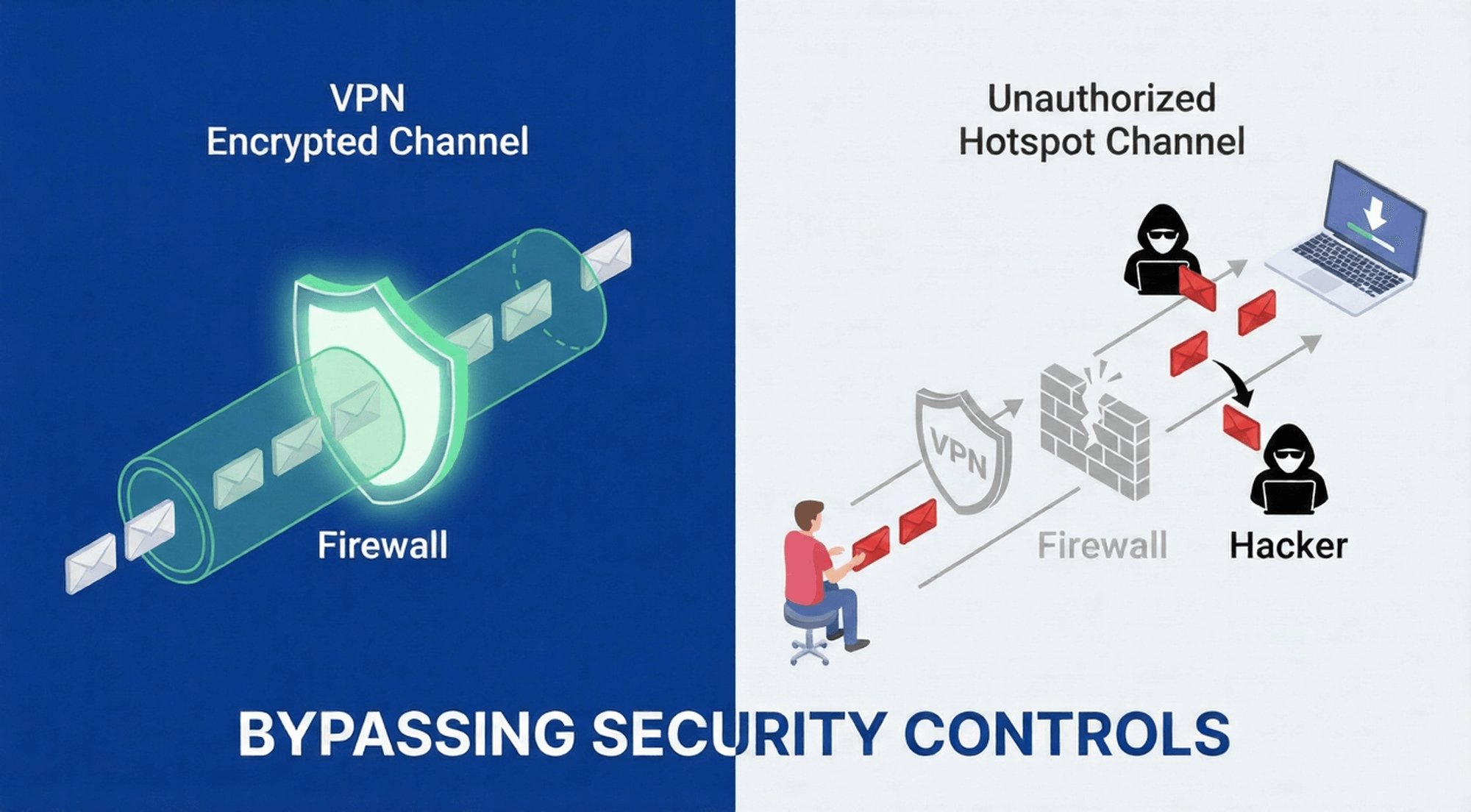
Enterprises deploy VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) and firewalls to ensure secure data transmission and compliant network access.
However, unauthorized hotspot sharing renders these core security tools completely ineffective, creating a major bypassing VPN risk, an unprotected data transmission channel.
The failure of the mandatory VPN policy
Most companies require employees to log in via VPN when accessing internal data from an external environment to ensure end-to-end encryption of data transmission.
However, unauthorized hotspot sharing completely circumvents this requirement: employees can directly access corporate business systems and download sensitive files by connecting their personal devices to the company's hotspot without logging into the VPN.
In this case, data transmission is unencrypted and extremely vulnerable to interception, tampering, or theft by hackers during transmission.
Firewalls and content filtering are practically useless.
The core function of a firewall is to block malicious websites and hacker attacks, while content filtering is used to restrict non-work-related network access (such as gambling websites and illegal download platforms).
However, network traffic transmitted through unauthorized hotspots completely escapes the monitoring scope of firewalls and content filtering: employees can use personal devices connected to these hotspots to access high-risk websites that are prohibited by the company and download malicious programs.
Hackers can also use this channel to implant viruses into company devices, which the firewall cannot identify or block. This situation also complicates shadow network management, as IT teams cannot track hidden or unauthorized traffic paths.
To facilitate working from home, a researcher at a technology company turned on a company-issued laptop (connected to the company intranet) as a hotspot for his personal mobile phone.
When his phone accessed an illegal software download website through the hotspot, it became infected with a data-stealing Trojan. This Trojan then used the hotspot connection to infiltrate the company laptop, stealing unpublished product source code and resulting in the leakage of core technologies.
Secure Your Network with AirDroid Business
Prevent unauthorized hotspot sharing and protect your enterprise from data leaks and security breaches. AirDroid Business offers robust controls to ensure secure network access.
3Risk 3: Direct Threat to Data Compliance – A “Match of Failure” for the Regulatory Industry

In industries such as healthcare (regulated by HIPAA) and retail payments (regulated by PCI-DSS), unauthorized hotspot sharing is not merely a "risk," but a "fatal violation" that directly leads to the failure of compliance audits. Enterprises engaging in such practices face increased enterprise data compliance risk, jeopardizing regulatory standing.
A fatal flaw in HIPAA compliance (healthcare industry)
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) explicitly requires "comprehensive control and traceability of patient data transmission channels," prohibiting any unauthorized or unencrypted transmission.
Unauthorized hotspot sharing in the healthcare industry precisely violates this core provision: nurses using nursing tablets (enterprise devices) to create hotspots for personal phones to view patients' electronic medical records (EHRs); doctors using hotspots to connect to personal computers to transmit surgical plans and patients' private data—these actions lack compliance approval, the data transmission paths are untraceable, and if discovered during an audit, will be directly deemed a compliance failure. These practices further elevate HIPAA violation risk, making regulatory breaches more likely.
Payment data risks under PCI-DSS regulation (retail/financial sector)
PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) mandates that "payment data transmission must be in an isolated and encrypted secure environment," prohibiting the transmission of credit card information and transaction records through public networks or unauthorized channels.
However, if POS terminals in retail stores and mobile payment devices in financial institutions are used for hotspot sharing, this isolation will be directly compromised.
Employees connecting to the hotspot with their personal devices may directly access customer payment card data in the POS system or transmit transaction records through the hotspot, exposing payment data to an unprotected environment. Such misuse severely impacts PCI-DSS mobile device compliance, undermining secure payment standards.
In 2023, a medical institution was fined $1.2 million after HIPAA audits found that nurses frequently used work tablets to transmit patient medical records via hotspots.
A chain supermarket's POS terminal hotspot sharing led to the leakage of 30,000 customer credit card information records. The chain was not only fined $800,000 by PCI-DSS, but also had to compensate customers for their losses, and its brand reputation was severely damaged.
4Risk 4: Device Infection and Malware Propagation – Lateral Penetration of Enterprise Networks
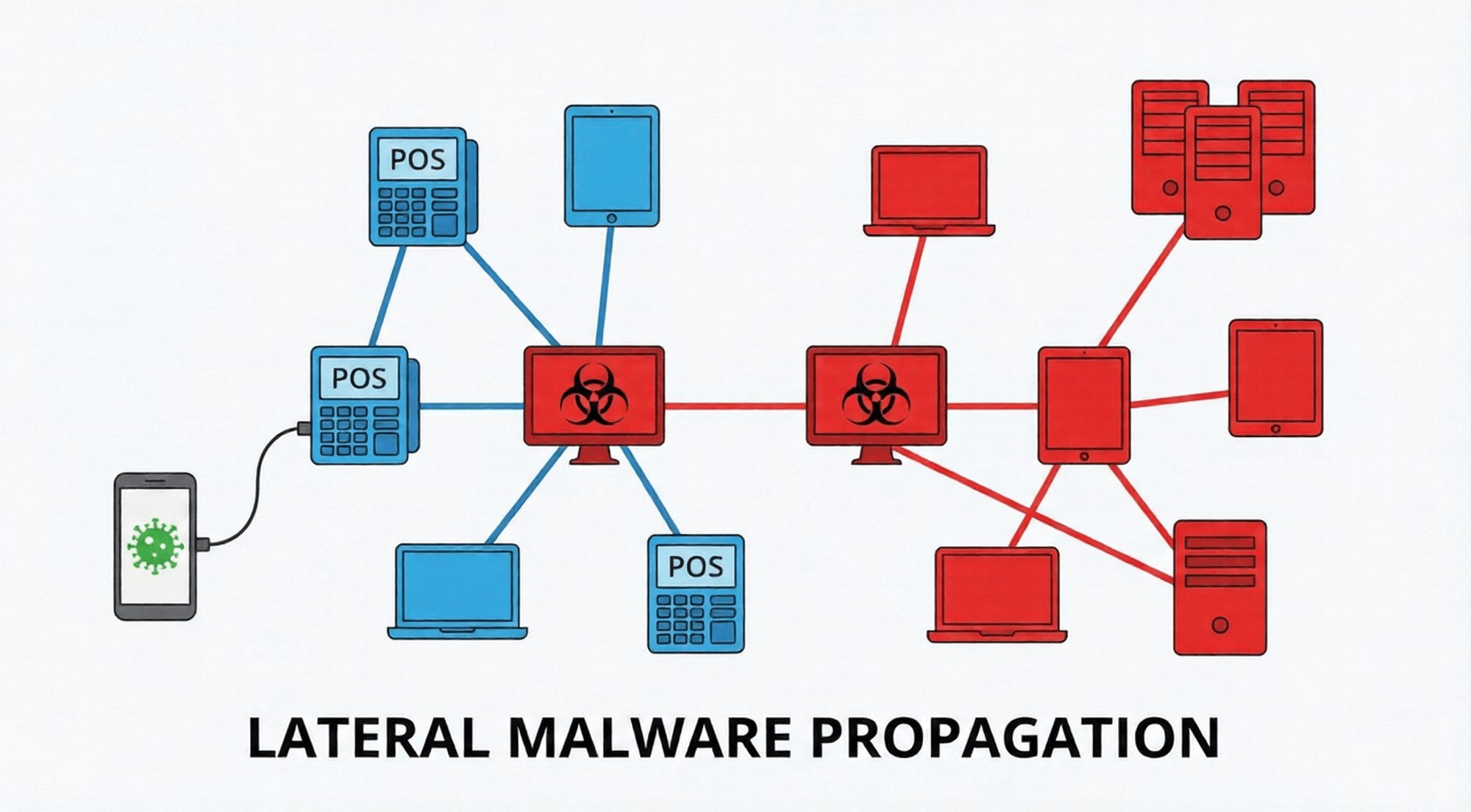
Unauthorized hotspot sharing becomes a "bridge" for malware to infiltrate corporate networks. Once one device is infected, the risk will quickly spread to the entire device fleet, triggering a systemic security crisis.
Additionally, the lack of proper segregation increases device network isolation difficulties, enabling wider malware spread.
Virus intrusion from infected external devices
External devices connected by employees (such as old personal computers or unsecured guest phones) may already be carrying malware such as Trojans, ransomware, and spyware.
Once these devices connect to corporate devices via hotspots, the malware automatically replicates and spreads to the corporate devices, completing the "first step" of the intrusion.
Because corporate devices are typically connected to the internal network, this facilitates the further spread of the malware.
Lateral penetration of malware into enterprise device networks
Once a company's device is infected, malware can use it as a node to laterally infiltrate other devices in the same network group.
If a POS terminal in a retail store is infected with ransomware, other terminals connected via hotspot will be encrypted simultaneously.
If a logistics company's field tablet is infected, it will spread the virus to the logistics tracking system and warehouse management equipment, causing business paralysis in the entire region.
These infections also increase audit traceability difficulty, making it harder for compliance teams to identify root causes.
A logistics company's field drivers turned on their work tablets as hotspots and connected them to personal mobile phones infected with ransomware. After the virus quickly infiltrated the tablets, it simultaneously infected 12 logistics tracking devices on the same route via the company's intranet, resulting in the loss of cargo location data, disruption of delivery routes, and direct losses of nearly one million yuan due to logistics delays.
Protect Your Devices with AirDroid Business
Stop malware in its tracks with AirDroid Business. Our MDM solution provides real-time monitoring and anomaly detection to keep your enterprise devices secure.
5Risk 5: Network resource abuse and business service interruption – a double loss in operating costs and efficiency.

Unauthorized hotspot sharing not only poses security risks but also consumes a large amount of enterprise network resources, causing core business service interruptions and increasing unnecessary operating costs.
Bandwidth contention caused core business processes to lag.
External devices connected via hotspots may engage in high-bandwidth-consuming activities for non-work purposes, such as watching high-definition videos, downloading large files, and playing online games.
These activities can consume network bandwidth on enterprise devices, causing lag, delays, or even failures in core business operations (such as inventory synchronization in retail stores, uploading patient data from medical devices, and updating logistics routes).
For example, a pharmacy employee used a hotspot on the cash register to connect to a personal computer to download movies, causing the store's drug inventory system to malfunction, delaying restocking requests, resulting in a three-day shortage of popular drugs and a loss of nearly 100,000 yuan in revenue.
A hospital nurse used a nursing tablet to watch TV series, causing the equipment data in the intensive care unit to be unable to be uploaded to the electronic medical record system in real time, affecting the diagnosis and treatment of patients.
Excessive data costs and resource waste
Enterprises equip their devices with data plans specifically for business scenarios. Unauthorized hotspot sharing can lead to significantly excessive data usage.
A field tablet typically uses about 5GB of business data per month, but hotspot sharing can cause its monthly usage to soar to over 20GB. This not only incurs huge excess data costs for enterprises but also wastes valuable network resources on non-business activities, increasing operating costs without any business benefits.
6Solution: How MDM can precisely control and block the risk of hotspot sharing
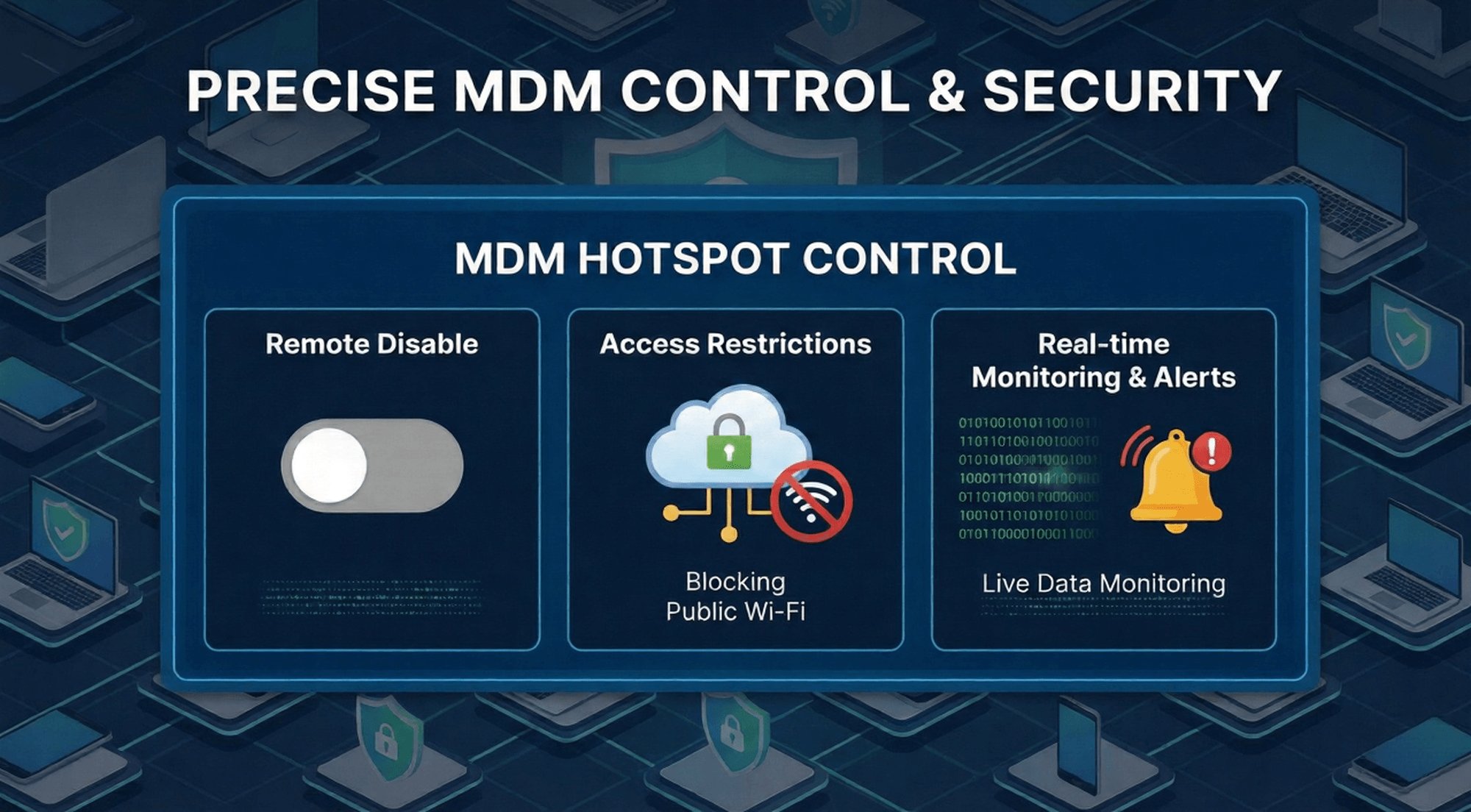
Faced with the multiple risks of unauthorized hotspot sharing, relying solely on verbal policies or employee self-discipline is insufficient to resolve the issue. Mobile Device Management (MDM) solutions (such as AirDroid Business) use technology to achieve end-to-end control over enterprise devices, preventing risks at the source while ensuring business flexibility.
MDM's core capabilities in hotspot management
AirDroid Business offers a triple-layer control system to address the risks of hotspot sharing: source disabling + real-time monitoring + anomaly blocking.
Remotely disable hotspot features
IT administrators can disable hotspot functionality for all or specific device groups in bulk through the backend, blocking unauthorized sharing at the source. Flexible configuration based on scenarios is supported: hotspots are disabled by default for field devices, and devices with special needs are set to "approval required for activation," ensuring that control does not affect legitimate business operations.
Network access restrictions
This feature restricts enterprise devices to connect only to pre-defined trusted networks (such as dedicated enterprise Wi-Fi or compliant VPNs), automatically blocking connections to untrusted networks such as hotspots and public Wi-Fi. If a device attempts to connect to an unauthorized network, the system will automatically disconnect and send an alert to the IT team.
Real-time monitoring and anomaly alerts
AirDroid Business tracks device network connectivity in real time: recording hotspot activation/deactivation times, connected external device information, data usage, etc.
Once abnormal behavior is detected (such as sudden hotspot activation, connection to unfamiliar devices, or a surge in data usage), an alarm is immediately triggered, allowing the IT team to remotely intervene (such as disabling the hotspot or locking the device).
Dual upgrades in compliance and security: more than just risk prevention
AirDroid Business's management capabilities not only prevent the risk of hotspot sharing, but also comprehensively improve a company's compliance and cybersecurity levels.
Construction of a Compliance Evidence Chain
It automatically generates hotspot usage logs, policy implementation records, and anomaly handling traces, supports the export of audit reports, and perfectly adapts to the audit requirements of regulations such as HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and GDPR, allowing enterprises to have "evidence to rely on" during compliance checks.
Malware Protection Collaboration
It can be integrated with enterprise security software to perform real-time security scans on devices connected via the network, and immediately block connections and isolate infected devices upon detecting malware to prevent the spread of risks.
Network resource optimization
Set a monthly data usage limit for the device and automatically alert the user when the usage approaches the threshold; monitor and restrict non-work-related network access to ensure that bandwidth resources are prioritized for core business and avoid waste and excessive costs.
Manage Hotspots Effectively with AirDroid Business
Gain full control over device hotspot usage with AirDroid Business. Implement end-to-end management to prevent risks and ensure compliance.
7Conclusion
Proactively prevent and control the risks of sharing hotspots, and strengthen the enterprise's security defense.
Unauthorized hotspot sharing is no trivial matter; it involves multi-dimensional security threats related to network boundaries, data transmission, compliance, device security, and resource management. Relying on employee self-discipline or verbal policies will only leave companies continuously exposed to risks—data breaches, compliance fines, and business paralysis could have severe consequences.
MDM solutions such as AirDroid Business use technology-driven, precise control to prevent the risk of hotspot sharing at its source: disabling unnecessary hotspot functions, restricting network access permissions, monitoring abnormal behavior in real time, and building a compliance evidence chain.
This "proactive prevention" model not only safeguards the company's cybersecurity and compliance bottom line but also avoids the impact of excessive control on business, achieving a balance between "security and efficiency."
In the digital age, enterprise equipment has become the core carrier of business operations, and its security is directly related to the survival and development of enterprises.
Regarding the hidden risk of unauthorized hotspot sharing, enterprises need to abandon the mentality of taking chances and establish a systematic prevention and control system through technical tools such as MDM (Multi-Demand Management) to build a solid cybersecurity defense and safeguard business development.







Leave a Reply.