Mandatory Access Control (MAC) for Enterprise MDM: Definition, Implementation & Scaling Guide
Today's work environments are increasingly fragmented: enterprises manage thousands of mobile devices across different regions, departments, and positions—each a potential entry point for data breaches. Traditional MDM configurations often act as "soft suggestions," easily bypassed by technically skilled employees, leading to the exposure of sensitive data. This is where Mandatory Access Control (MAC) comes in: it is a core pillar of enterprise mobile security, transforming company policies into unbreakable system-level rules.
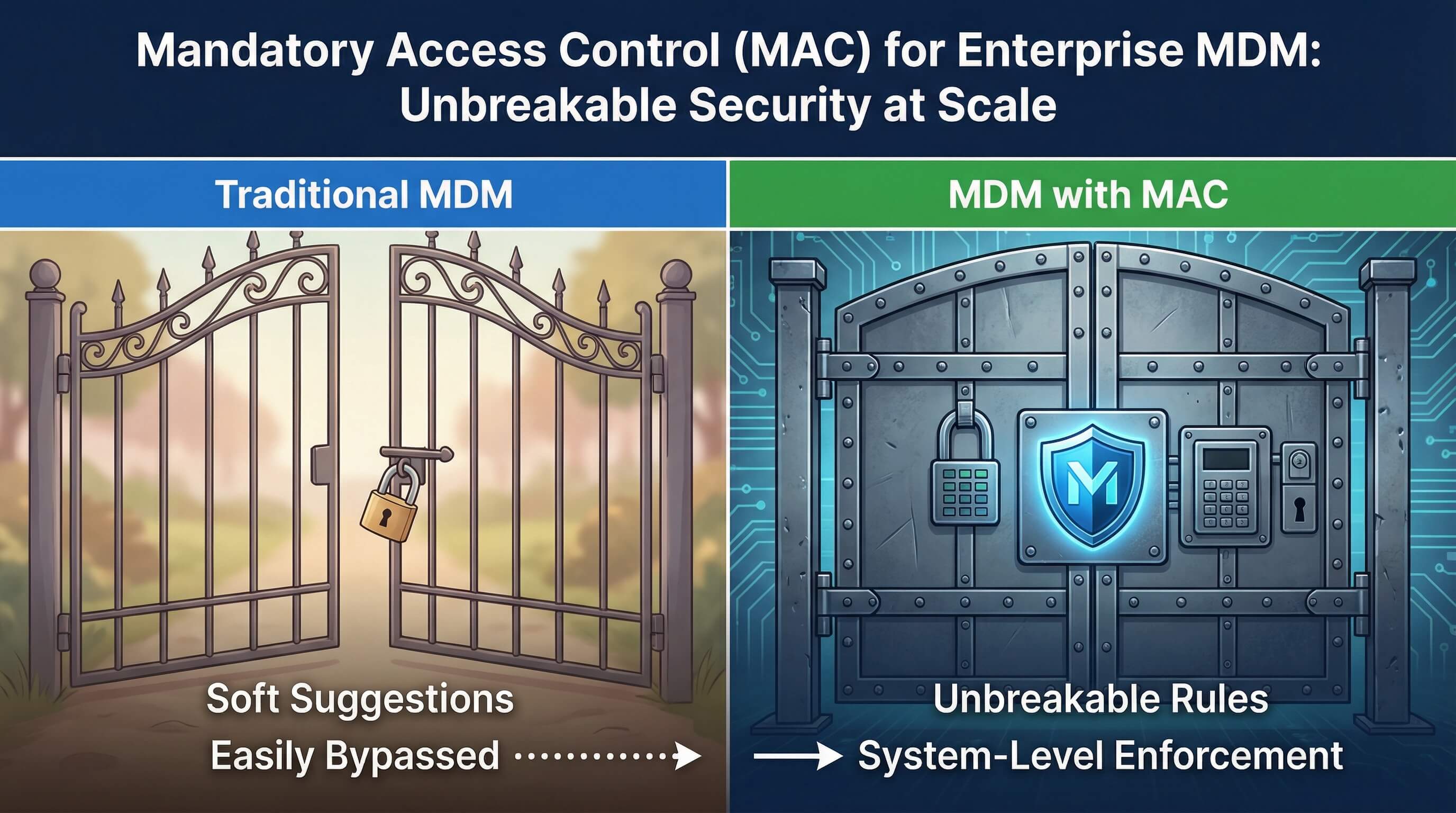
For teams using modern MDM tools like AirDroid Business, MAC is no longer just an esoteric computer theory, but a scalable, compliant, and business-aligned framework for protecting a fleet of Android and Windows devices.
- 1 : What Is Mandatory Access Control (MAC) in Enterprise MDM?
- 2 : 4 Types of Access Control: Why MAC Is Critical for Enterprises
- 3 : How Enterprise MDM Enforces "Unbypassable" MAC at Scale
- 4 : Step-by-Step Enterprise MAC Deployment with AirDroid Business
- 5 : Enterprise-Grade Flexibility: Exception Policies & Permission Lifecycle
- 6 : Enterprise-Grade Deep Practices: Solving Core Scaling Pain Points
- 7 : Enterprise Benefits: Security, Compliance & ROI
- 8 : Enterprise MDM MAC Tool Selection & Comparison
1What Is Mandatory Access Control (MAC) in Enterprise MDM?
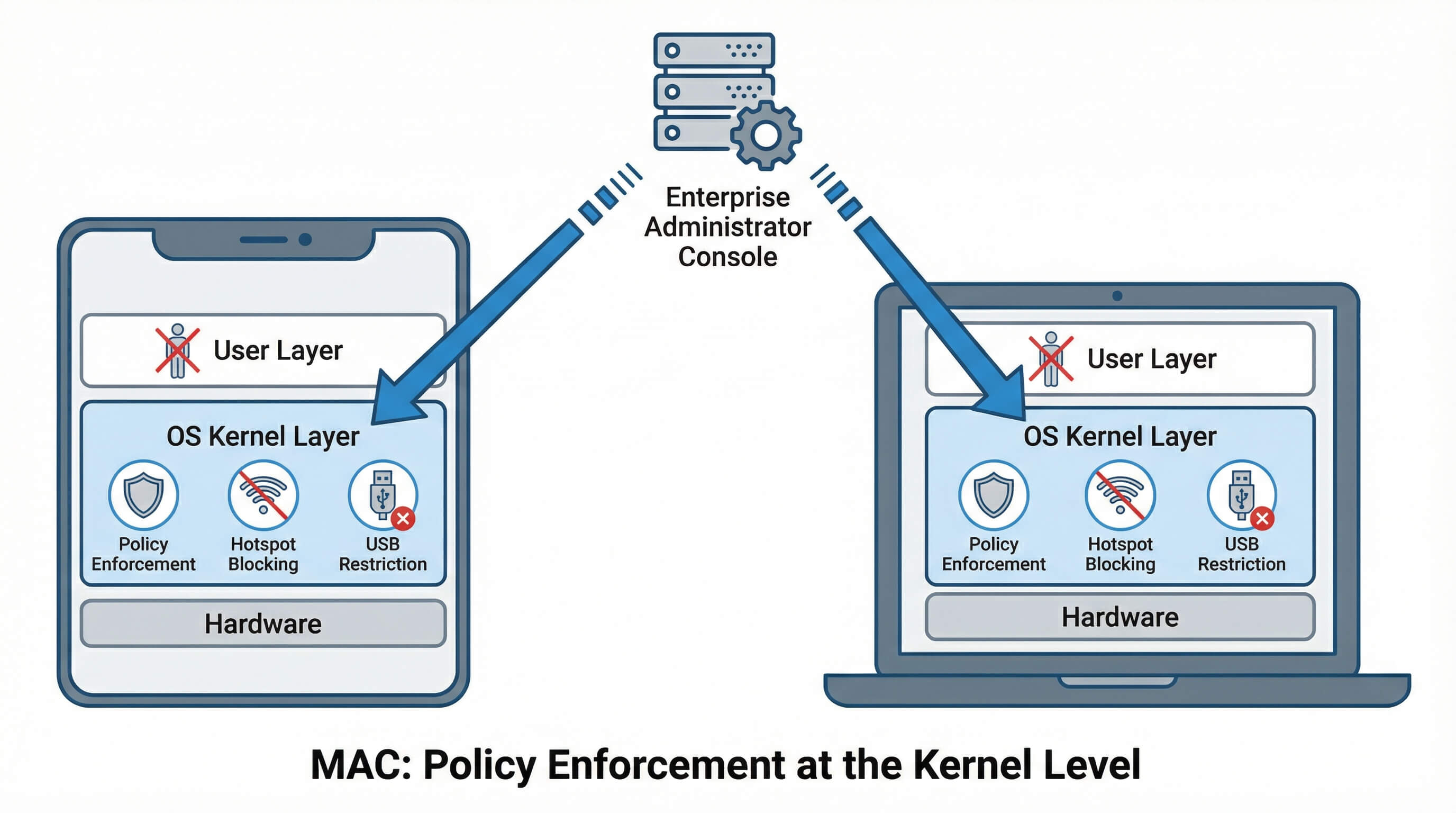
Core Definition of MDM Mandatory Access Control
Essentially, Mandatory Access Control (MAC) is an access control model where security policies are enforced at the operating system kernel level, and users have no right to override them. Unlike discretionary access models (where users retain control), MAC completely empowers enterprise administrators. For MDM, this means:
- Policies (such as disabling hotspots or blocking USB data transfer) are embedded in the device's hardware and software layers, rather than merely remaining at the surface level;
- Compliance is mandatory: even highly skilled employees cannot bypass rules through reboots, ADB commands, or factory resets;
- Supports large-scale management of thousands of devices, ensuring consistency in security policies across global teams.
AirDroid Business further integrates MAC with specific enterprise needs: centralized policy management, cross-regional deployment capabilities, and deep compliance support—transforming MAC from a technical concept into a practical solution for mobile device fleets.
MDM MAC vs. Regular MDM Configuration (Enterprise Perspective)
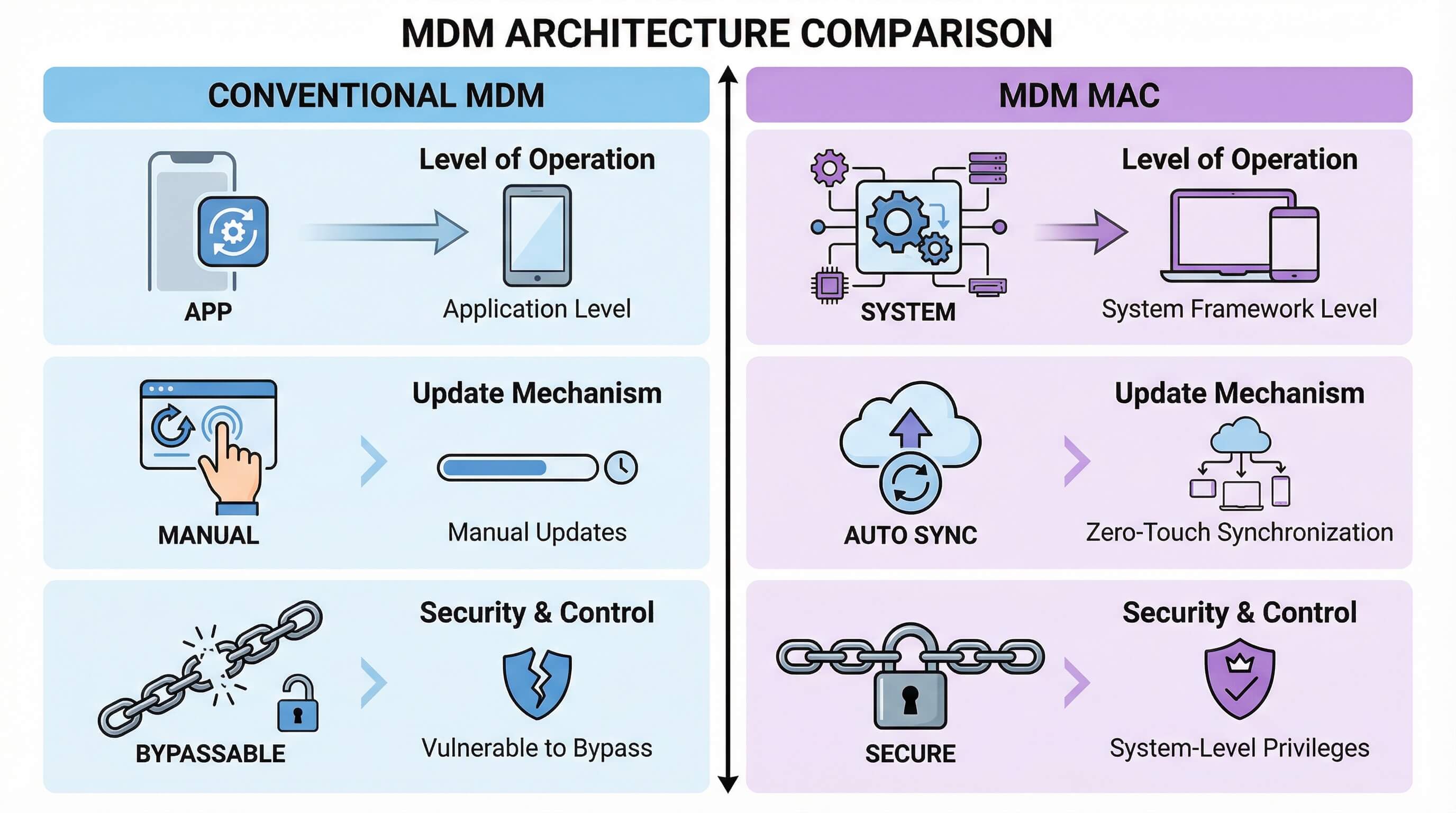
In enterprise scenarios, consistency and security cannot be compromised in the slightest. The difference between control under the MAC (Macro-Macro) approach and conventional MDM (Macro-Macro-Device) configuration is enormous. To illustrate this difference visually, please refer to the table below.
Comparison Dimension | Conventional MDM Configuration | MDM Mandatory Access Control (MAC) Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Control Level | Application level (can be bypassed by users through system settings) | System framework level (options are disabled/greyed out; no user interaction possible) |
| Scalability | Relies on manual updates, prone to errors | Supports large-scale deployment for thousands of devices with zero-touch synchronization |
| Bypass Resistance | Vulnerable to reboot, ADB debugging, and developer mode | Policies enforced by system-level privileges, preventing users from modifying critical settings |
| Compliance Support | Basic logging with limited tamper resistance | Encrypted, tamper-proof audit trails that directly meet compliance and audit requirements |
For businesses, this difference directly determines the level of risk: conventional MDM may only "discourage" the use of unauthorized hotspots, but MDM based on the MAC concept can completely "eliminate" them—this is an insurmountable security bottom line for industries such as finance, healthcare, and government that handle extremely sensitive data.
Device Owner Mode: The Foundation of Enterprise-Grade MAC
To unlock truly "unbreakable" capabilities, AirDroid Business Enterprise Edition employs proprietary core management technologies for different systems:
Android: Device Owner Mode

Device Owner Mode (DO Mode) represents the highest set of permissions in the Android system, granting AirDroid Business system-level control, which is crucial for enterprises:
- 1. Deep Permission Control: DO Mode allows administrators to directly access Android's management APIs, ensuring that high-risk operations such as Wi-Fi hotspots and USB debugging are effectively blocked before they are triggered.
- 2. Anti-Removal Mechanism: On enterprise-owned devices, combined with Android Zero Touch registration, even if the device is physically reset (factory reset), management will be forcibly reactivated as long as it is connected to the internet.
- 3. Large-Scale Activation: Provides multiple methods such as Zero Touch and QR code scanning, ensuring minute-level deployment across teams and regions.
Windows: Configuration Service Provider (CSP) and Group Policy Consistency

For Windows 10/11 devices, AirDroid Business enforces MAC rules through modern management protocols:
- 1. System-level restrictions: Blocks USB storage device mounting and disables unauthorized applications from running through system-level configuration;
- 2. Effective at boot: Policies are written to system configuration immediately after issuance, unaffected by reboots, and are loaded the moment the system starts.
24 Types of Access Control: Why MAC Is Critical for Enterprises
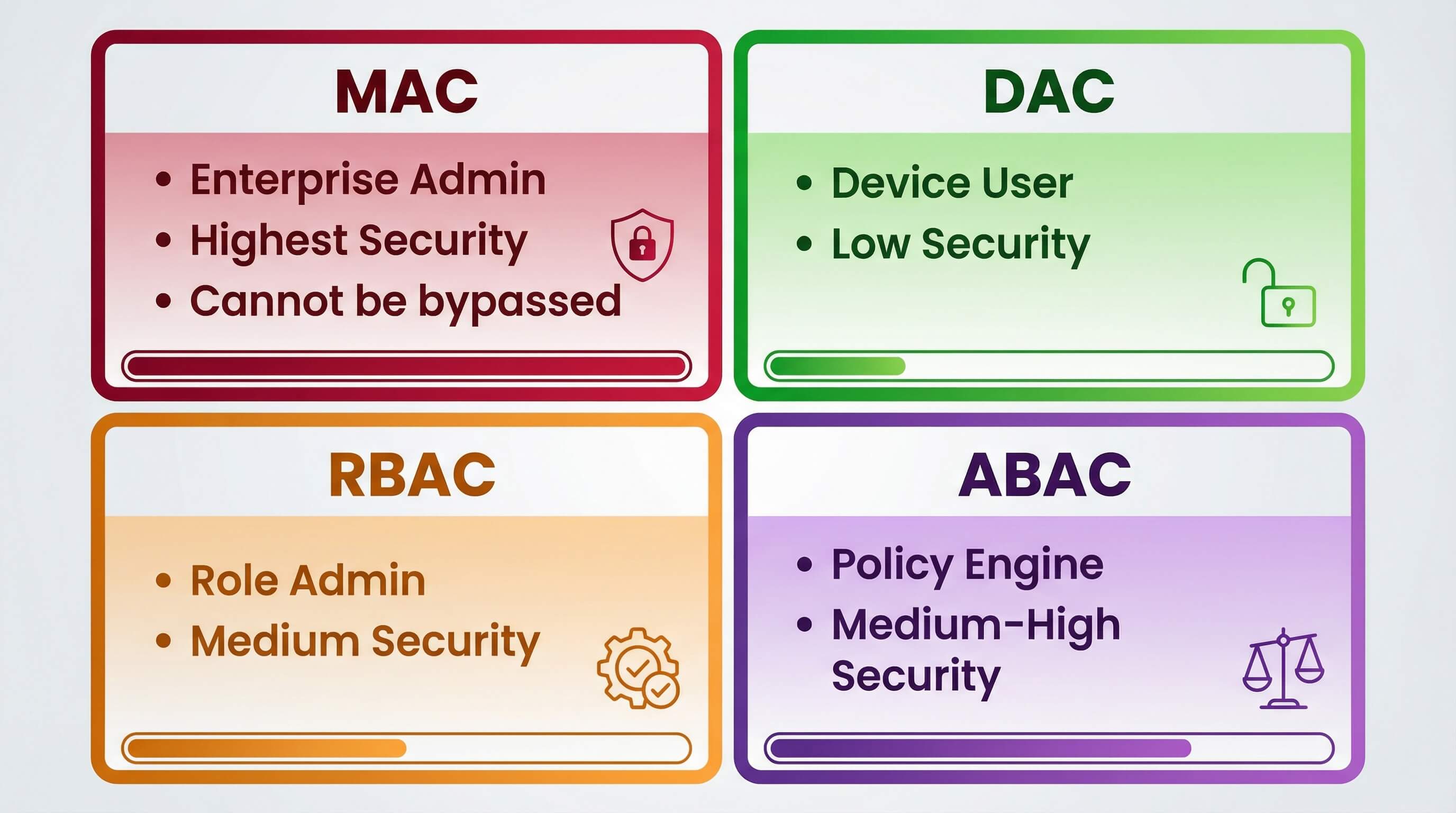
Overview of 4 Access Control Models (Enterprise Use Cases)
Enterprises have four mainstream access control models to choose from, but only MAC can meet the unique challenges of managing large-scale mobile devices:
Model | Control Owner | Enterprise Suitability | Security Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mandatory Access Control (MAC) | Enterprise administrator | High (finance, healthcare, government) | Highest (cannot be bypassed) |
| Discretionary Access Control (DAC) | Device user | Low (suitable for personal or individual work devices) | Low (user-controlled) |
| Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) | Role administrator | Good (internal permission hierarchy) | Medium (role-dependent) |
| Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) | Policy engine | Good (dynamic, context-aware control) | Medium to High |
MAC vs. DAC/RBAC: Enterprise Security Trade-Offs

For businesses, choosing a management model essentially involves finding a balance between security, flexibility, and compliance:
MAC vs. DAC: DAC often relies on employee self-discipline (e.g., "Please don't turn on your hotspot"), but in a corporate environment, a single oversight can lead to millions in losses. MAC directly eliminates human error.
MAC vs. RBAC: RBAC solves the "who can see what" problem, but it can't prevent users from abusing existing legitimate functions.
AirDroid Business cleverly solves this problem by using "strong MAC control + flexible RBAC allocation":
1. MAC Base Layer: System-level blocking of high-risk operations (forcefully disabling USB data transfer, blocking unauthorized apps).
2. RBAC Flexible Layer: Granting different exception permissions based on roles (e.g., field staff vs. office staff). This hybrid model maintains the security baseline of "default denial" while ensuring smooth legitimate business operations.
3How Enterprise MDM Enforces "Unbypassable" MAC at Scale
Low-level enforcement on Android + Windows devices
AirDroid Business offers customized policy enrollment solutions for the security architectures of both operating systems:
Android: Leveraging device owner mode, it directly blocks Wi-Fi hotspot sharing, USB debugging, and screen recording. For different Android versions, AirDroid Business ensures over 90% control coverage through compatible APIs.
Windows: By locking system configurations, it implements application whitelisting and peripheral restrictions. The policies take effect synchronously with system security patches, ensuring seamless protection.
Can Enterprise Users Bypass MAC? (Reboot/Factory Reset/ADB)
This is the most pressing question for IT administrators. For AirDroid Business users, the answer is clear: no.
Reboot Immunity: The policy exists in the system's persistent configuration; a reboot will only trigger a policy reload.
Factory Reset Immunity: With Android Zero Touch, a reset device will automatically reconnect and reinstall the AirDroid Business client.
Anti-Tampering Detection: ADB debugging is blocked by default. If someone attempts to tamper with the policy using technical means, an alert will be immediately triggered in the console.
Cross-Region/Cross-Network Deployment for Global Enterprises
Multinational enterprises face numerous challenges when deploying MAC (Machine Access Control) systems: devices in remote offices, isolated intranet environments, and even offline field operations—AirDroid Business addresses these challenges with enterprise-grade tools:
- Offline Policy Synchronization: Field devices (such as delivery tablets and factory terminals) automatically receive policy updates after connecting to the network, requiring no manual intervention;
- Differential Updates: Only policy changes are pushed, reducing bandwidth consumption; updates for thousands of devices take less than 5 minutes; A European retail chain managing 5,000 Android + Windows devices across 10 countries used AirDroid Business to reduce cross-regional MAC deployment time from 2 weeks (manual) to 1 day (automated)—and achieved 100% policy consistency.
4Step-by-Step Enterprise MAC Deployment with AirDroid Business
Prerequisites for Enterprise-Grade Deployment
Before officially implementing mandatory controls, companies are advised to make the following preparations:
- 1. Device Fleet Mapping: Categorize devices by system version and usage scenario (e.g., "warehouse barcode scanners," "financial office notebooks").
- 2. Compliance Mapping: Translate industry regulations (such as GDPR) requirements into specific MDM switch settings.
Batch deployment of the "Hotspot/USB blocking" basic policy
The following are typical steps to disable hotspots and block USB transfers on thousands of devices in batches:
- Step 1: Create a system template. Log in to the console and create "Core Management Templates" for both Android and Windows in the "Policies & Kiosks" section, enabling switches such as "Disable USB Transfers".
- Step 2: Assign to target groups. Select the template you just created and apply it to the "Retail Terminals" or "Sales Field Staff" device group with one click.
- Step 3: Automated deployment. After clicking deploy, the system will automatically distribute the policy to all online devices, and offline devices will automatically complete the policy the next time they come online.
5Enterprise-Grade Flexibility: Exception Policies & Permission Lifecycle
Tiered Policy Structure (Global→Regional→Departmental)
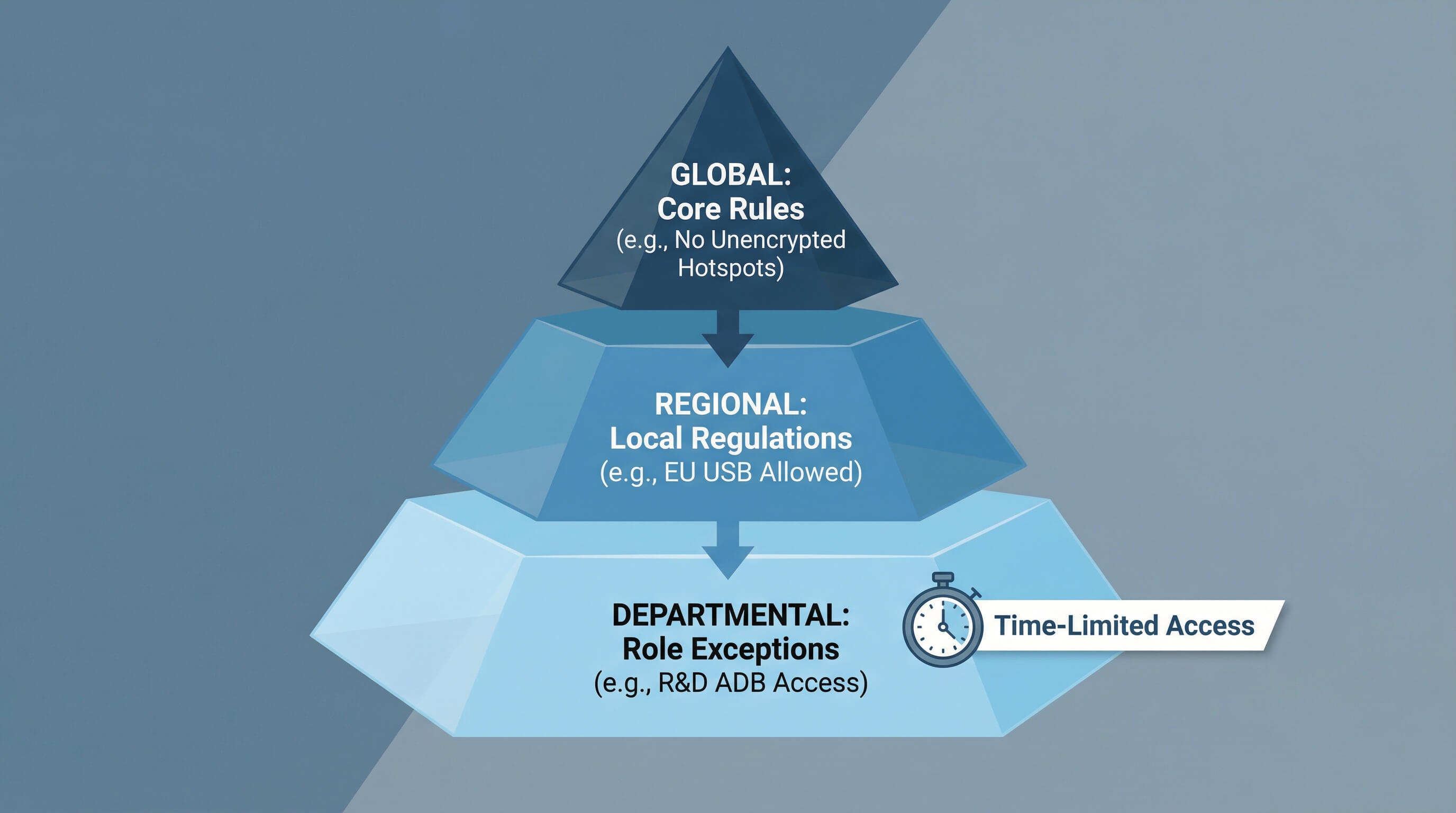
Enterprises don't need a "one-size-fits-all" MAC strategy. AirDroid Business supports a layered architecture, balancing global compliance and local flexibility:
- Global Layer: Core rules uniformly followed across all Android/Windows devices (e.g., disabling unencrypted hotspots);
- Regional Layer: Adapting to local regulations (e.g., allowing USB transfers in EU branches);
- Departmental Layer: Role-based exceptions (e.g., allowing R&D teams to use ADB/registry editing, with time limits).
A policy inheritance mechanism ensures that regional/departmental rules do not violate global compliance requirements—for example, temporary hotspots for the sales team must be encrypted and comply with GDPR standards.
Scenario-Based Exception Authorization (Sales/R&D/Field Teams)
MAC isn’t synonymous with inflexibility. AirDroid Business's scenario-based exception licensing can adapt to the needs of different teams: Field Sales: Allow limited-time access to encrypted hotspots for business demonstrations.
Hospital IT: Temporarily open specific USB ports for data reading, but the entire operation is logged in the audit log.
In this way, MAC maintains security while ensuring normal business operations aren't disrupted.
6Enterprise-Grade Deep Practices: Solving Core Scaling Pain Points
Integration with Enterprise Security Ecosystem (EDR/IAM/SIEM)
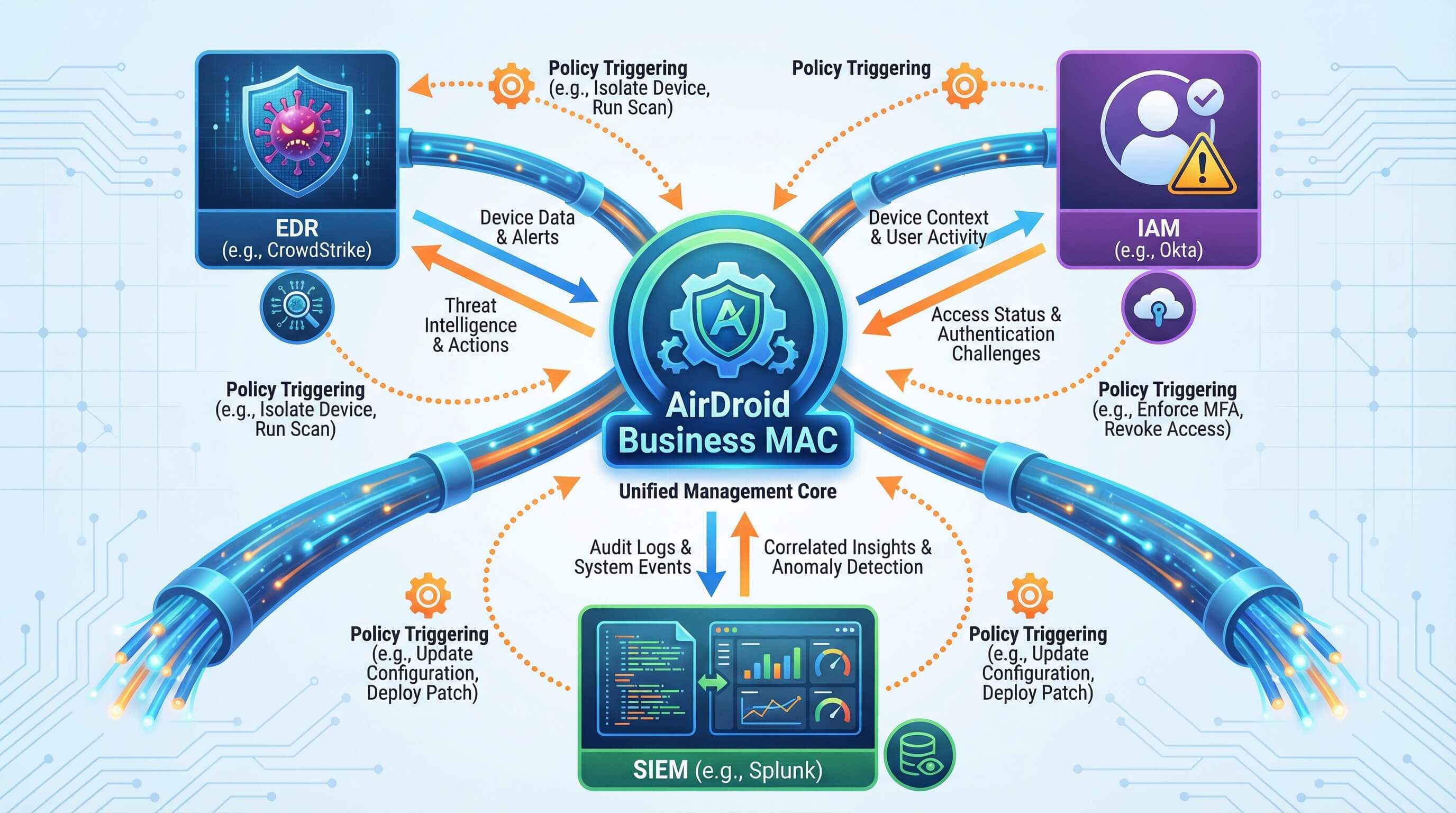
MAC does not operate in isolation. AirDroid Business integrates seamlessly with leading enterprise security tools:
- EDR integration (e.g., CrowdStrike): When EDR detects malware, AirDroid Business immediately triggers full MAC restrictions to prevent data leakage.
- IAM integration (e.g., Okta): If a user shows high-risk login behavior (such as a login from an unusual location), MAC policies are automatically tightened (for example, temporarily disabling hotspot access).
- SIEM integration (e.g., Splunk): MAC-related alerts (bypass attempts, policy violations) are synchronized to the SIEM console, enabling cross-platform correlation and analysis.
Industry-Specific Compliance Mapping (Finance/Healthcare/Government)
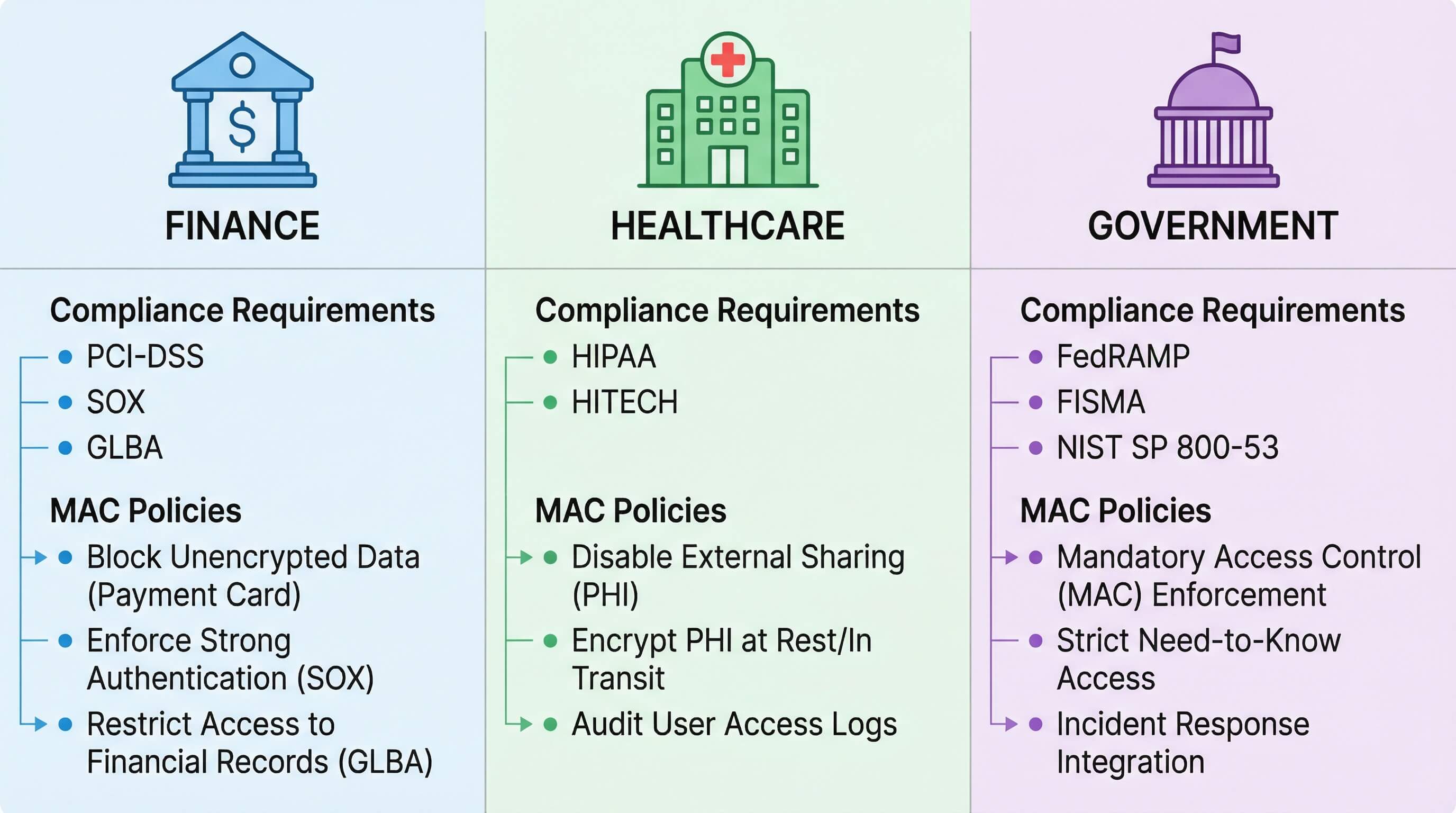
Compliance requirements vary across industries, and AirDroid Business provides targeted MAC policy mapping to address these differences.
Industry | Compliance Requirement | MAC Policy |
|---|---|---|
| Finance (PCI-DSS) | Block unencrypted data transmission | Disable unencrypted hotspots and USB access; allow only whitelisted applications |
| Healthcare (HIPAA) | Protect electronic protected health information (ePHI) | Disable all external sharing functions on devices storing ePHI |
| Retail | POS device security | Enable kiosk mode on Android and Windows devices; restrict access to authorized applications only |
Large-Scale Change Risk Control
When implementing large-scale policy updates, AirDroid Business offers a "phased deployment" capability. You can pilot it on 10% of your devices first to ensure it doesn't impact your business before proceeding with the full rollout.
7Enterprise Benefits: Security, Compliance & ROI
Risk Mitigation: Statistics show that implementing mandatory access control policies can reduce data breaches on enterprise mobile devices by over 90%.
Compliance Simplification: Automated audit report generation reduces the time required to respond to PCI-DSS or GDPR audits from weeks to days.
Cost Reduction and Efficiency Improvement: IT support tickets have been reduced by over 40%, eliminating the need for IT staff to handle issues caused by employee misconfigurations on each device.
8Enterprise MDM MAC Tool Selection & Comparison
Key Features to Evaluate for Enterprise MDM MAC
When evaluating MDM solutions with Mandatory Access Control (MAC) capabilities, enterprise IT decision-makers should prioritize the following five key dimensions:
- System-Level Enforcement Depth:
Whether the solution can truly disable system settings (such as greying out switches) rather than relying only on application-layer warning prompts. - Large-Scale Enrollment Efficiency:
When managing mixed fleets of thousands of devices or more, whether policy enforcement can synchronize and take effect within seconds. - Security Ecosystem Integration:
Whether audit logs can be pushed in real time to SIEM platforms (such as Splunk) or integrated with existing IAM systems. - Risk Mitigation and Fault Tolerance:
Whether the solution supports phased deployment and one-click rollback to prevent large-scale business disruptions caused by incorrect enforcement of mandatory policies.
Comparison of Top MDM Solutions (AirDroid Business/Intune/Soti)
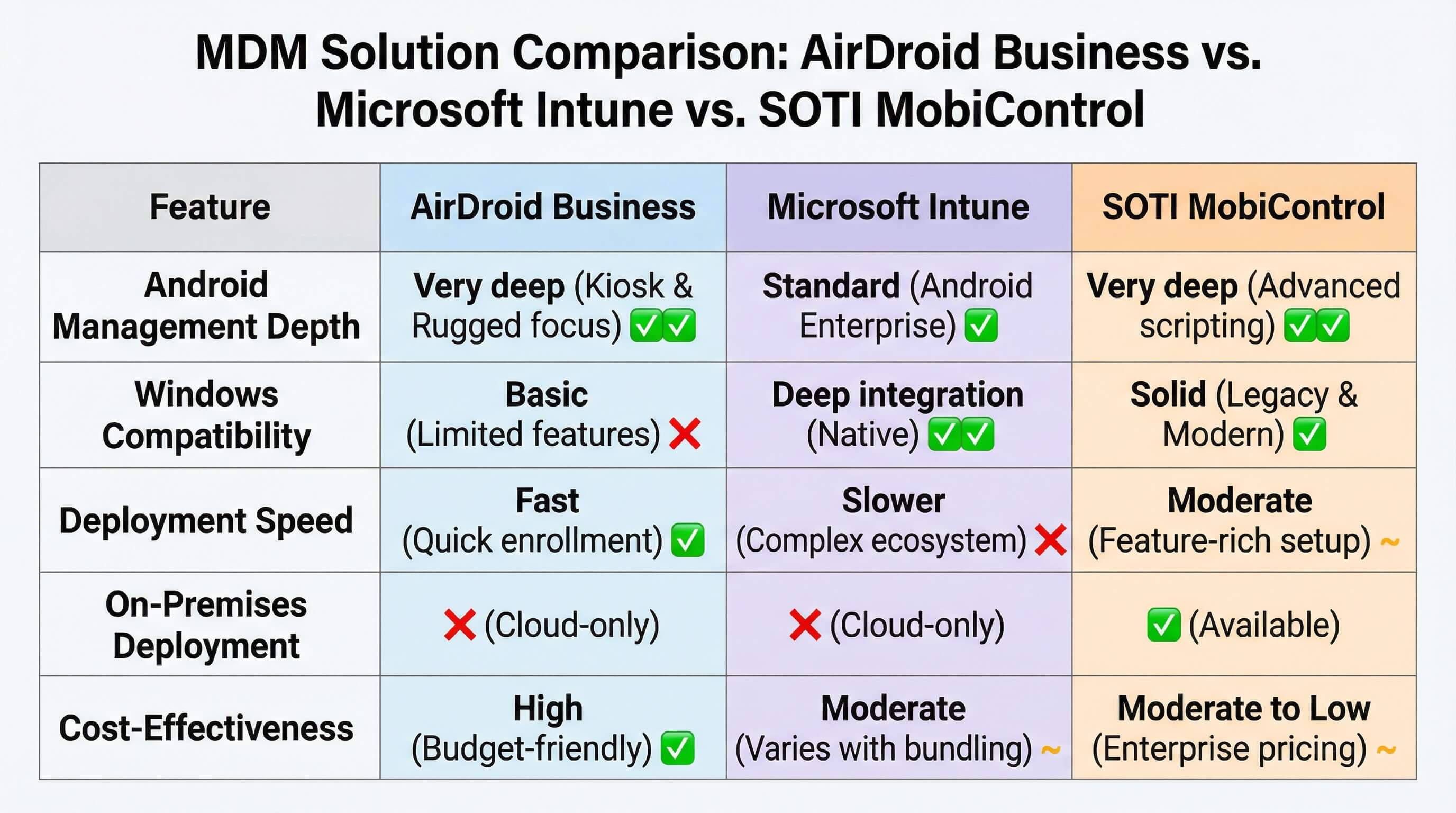
When selecting a solution, businesses typically weigh AirDroid Business against Microsoft Intune and Soti MobiControl. While all offer management capabilities, they each emphasize different aspects of achieving a balance between "mandatory" and "easy-to-use":
Feature Dimension | AirDroid Business (Enterprise Edition) | Microsoft Intune | SOTI MobiControl |
|---|---|---|---|
| Android Management Depth | Very deep: Focused on the Android ecosystem with extensive support for manufacturer-specific APIs enabling deep system-level locking | Standard: Relies on Android Enterprise framework with limited optimization for non-mainstream brands | Deep: Strong OEM partnerships supporting advanced customization |
| Windows Compatibility | Supports Windows 7 / 10 / 11, covering both legacy and modern assets | Excellent support for Windows 10 / 11, limited support for legacy systems | Broad support, including legacy Windows CE/Mobile devices |
| Deployment & Policy Effectiveness Speed | Very fast: Lightweight architecture enables synchronization of large-scale policy changes within minutes | Slower: Policy deployment relies on polling cycles; large-scale rollouts may take longer | Moderate: Powerful features but complex configuration requiring higher IT expertise |
| On-Premises Deployment | Supported: Meets data residency requirements for highly regulated industries | Not supported: Cloud-only deployment via Azure | Supported: Offers private deployment options |
| Cost-Effectiveness (ROI) | Very high: Transparent per-device pricing without requiring bundled licenses | Medium: Often tied to Microsoft 365 licensing, increasing costs for organizations not fully invested in the Microsoft ecosystem | Lower: Traditional enterprise pricing with higher costs for add-on services |
Selection Conclusion: Why is AirDroid Business the optimal solution for an Android + Windows fleet?
Intune: While powerful, its depth of customization and control over the Android underlying layer is often inferior to AirDroid Business, and its cost structure is complex.
Soti: Has an extremely high configuration threshold, resulting in a significant learning curve for medium to large enterprises prioritizing efficiency.
AirDroid Business: Balances "enterprise-level mandatory depth" with "internet-friendly ease of operation," supporting high-speed response on tens of thousands of devices.
The conclusion is very clear:
If your company is already deeply integrated with the Microsoft ecosystem and has a sufficient budget, Intune is the natural choice;
If you need to manage a large number of old, specialized industrial devices, Soti has deep technical expertise;
However, if your goal is to implement "unavoidable" mandatory security policies on tens of thousands of modern Android and Windows devices in the most efficient, intuitive, and cost-effective way, AirDroid Business is undoubtedly the current market balance point. It simplifies complex MAC theory into daily operations that IT managers can complete with a few clicks of the mouse.
9Conclusion
Scale Enterprise Mobile Security with AirDroid Business MAC
In the mobile-first era, mandatory access control (MAC) is no longer an option, but a moat protecting enterprise digital assets. AirDroid Business Enterprise Edition transforms complex technology into an easy-to-deploy, unavoidable management tool.
Ready to upgrade your device security? Apply for a free AirDroid Business Enterprise Edition demo today and experience true "enterprise-grade mandatory control."
FAQs







Leave a Reply.