Best Practices for Corporate Mobile Data Management
- 1 : The urgency and core objectives of enterprise mobile data management
- 2 : Best Practice 1: Build a "Comprehensive" Mobile Access Control Framework
- 3 : Best Practice 2: Shifting from a "Reactive Firefighting" to a Mobile device proactive management Model
- 4 : Best Practice 3: Prove the Value of Mobile Data Management with Quantitative ROI
- 5 : Best Practice 4: Differentiated Implementation Strategies Based on Industry Characteristics
The urgency and core objectives of enterprise mobile data management
According to Gartner's 2024 Enterprise Mobile Device Security Report, 78% of enterprises have experienced at least one compliance penalty or data breach due to improper mobile data management, with an average loss exceeding $1.2 million per incident.
As Android devices become increasingly prevalent in enterprise scenarios POS terminals in retail stores, tracking tablets in logistics fleets, and nursing equipment in hospitals, have become core carriers of business operations the risks of mobile data misuse and leakage are becoming increasingly prominent.
For example, a chain retail company suffered a PCI-DSS fine of $800,000 after an employee unauthorizedly enabled a POS terminal hotspot, resulting in the leakage of 30,000 customer payment records. A logistics company incurred additional communication costs of 450,000 yuan in 2023 alone due to excessive data usage on field tablets.
Traditional fragmented management (such as verbally prohibiting hotspots and manually checking bills monthly) is no longer sufficient to manage large-scale devices. Enterprises urgently need to shift from reactive firefighting to proactive system building, balancing three core objectives through standardized best practices: data security (preventing leakage risks), cost control (avoiding excessive spending), and business flexibility (not affecting normal operations).
Mobile Device Management (MDM) solutions (such as AirDroid Business) are the core tools for realizing these objectives they can transform abstract management strategies into actionable actions on devices, helping to achieve more comprehensive control, more effective risk prevention, and clearer value quantification. This aligns closely with modern Corporate mobile security policy requirements and drives organizations toward Enterprise mobile governance best practices.

Enhance Mobile Data Management with AirDroid Business
Discover how AirDroid Business can help you achieve data security, cost control, and business flexibility. Transform your mobile data management strategy with our comprehensive MDM solution.
Best Practice 1: Build a "Comprehensive" Mobile Access Control Framework
The essence of mobile data breaches often lies in the lack of control over a single risk entry point this could be a hotspot opened by an employee or a USB flash drive plugged into a device. Therefore, effective data management must establish a comprehensive access control framework, incorporating hotspot disabling into a unified system and simultaneously managing all potential risk points such as ports, applications, and networks, all while adhering to a "Zero Trust mobile policy" principle: never defaulting to any device function or user action, and requiring all access to be authorized by policy.
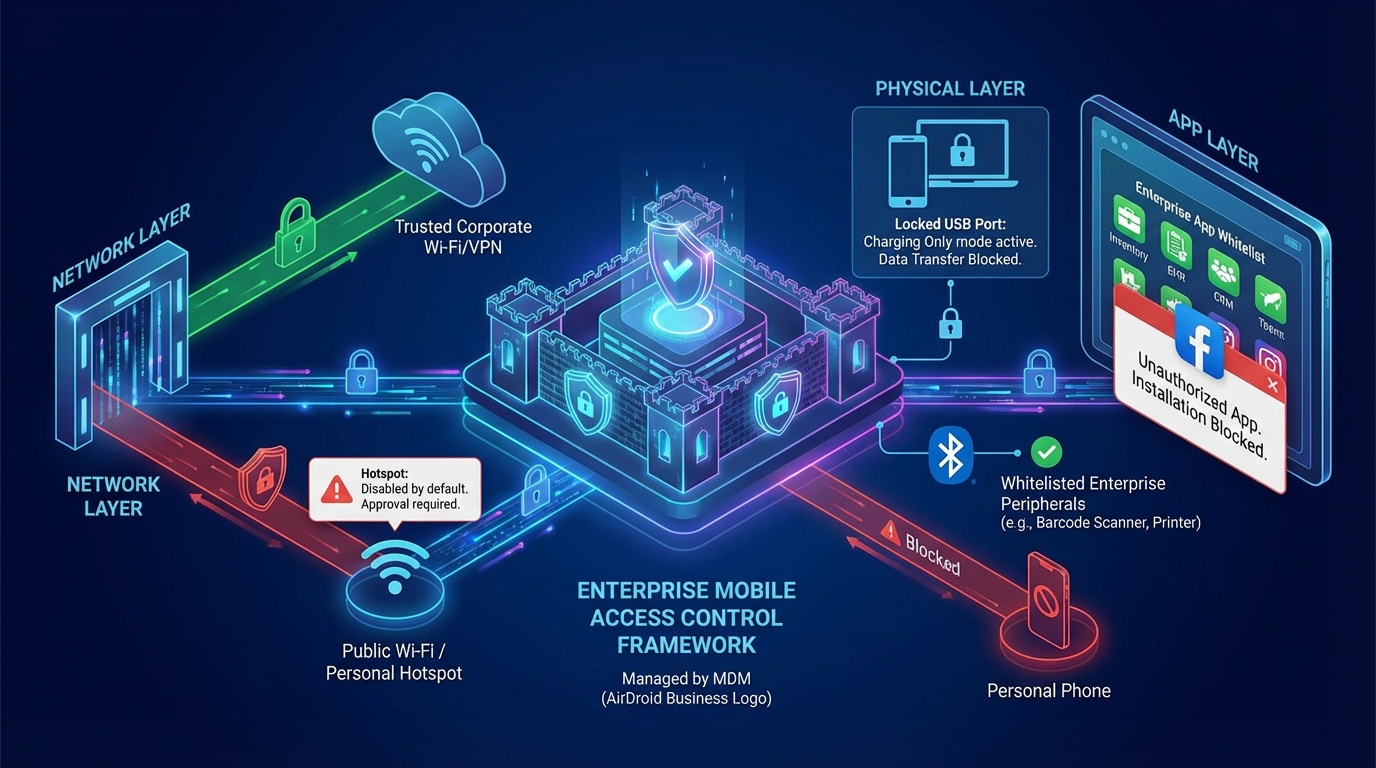
Hotspots and Network Access: Blocking Untrusted Data Transmission Paths
Hotspots are a "high-risk entry point" for enterprise mobile data leaks—employees may enable hotspots on their work devices for personal convenience, leading to the transmission of customer data and transaction records through unencrypted hotspot networks. Embedding hotspot control into network access policies requires a closed loop, moving from default disabling to controlled authorization:
1. Default Disabling + Approval Authorization:
Using MDM (such as AirDroid Business), batch-set the hotspot function of all enterprise devices to "disabled by default." Only when employees have legitimate business needs (such as field staff synchronizing data at construction sites without enterprise Wi-Fi) can they submit an application through the employee app, explaining the usage scenario and duration (e.g., "complete inventory synchronization within 2 hours"). After online review and approval by the IT team, hotspot permissions are temporarily unlocked, and automatically disabled upon expiration. After adopting this model, a construction company saw a significant reduction in hotspot violation rates from 35% to near zero.
2. Network Access Whitelist:
Restrict devices to access only pre-approved trusted networks, including enterprise Wi-Fi and compliant VPNs. If a device attempts to connect to unauthorized networks such as public Wi-Fi or personal hotspots, MDM (such as AirDroid Business) will automatically block the connection and send an alert to the IT team, while simultaneously displaying a pop-up message to employees stating, "The current network is insecure; please switch to the company Wi-Fi." A healthcare company used this feature to avoid the risk of patient record leaks caused by nursing tablets connecting to public Wi-Fi in wards.
3. Network Behavior Logging:
Records all network switching behavior of the device. These logs can not only be used for compliance audits but also provide crucial clues for locating the source of risk in the event of a data breach. For example, a financial company discovered through logs that an employee was using their work phone's hotspot to connect to their personal computer and download customer information outside of work hours, thus promptly preventing the leak.
Port and peripheral control: plugging data vulnerabilities at the physical layer
Physical ports (such as USB and Bluetooth) are easily overlooked "data exit points"—employees may copy business data from devices via USB flash drives or transfer sensitive files to personal mobile phones via Bluetooth. Therefore, port management needs to achieve "functional segmentation + authorized use":
1. Fine-grained USB port management:
Some advanced MDM tools support splitting USB port functions into 'charging mode' and 'data transfer mode,' with only 'charging mode' enabled by default, disabling data transfer. After adopting this strategy, a retail company effectively curbed and significantly reduced violations involving copying POS terminal transaction data via USB.
2. Bluetooth device whitelist:
Restrict Bluetooth connections to only enterprise-certified peripherals, such as wireless barcode scanners and dedicated printers, prohibiting pairing with personal mobile phones, headphones, and other non-work devices. AirDroid Business supports importing a whitelist of enterprise peripheral MAC addresses; devices can only recognize and connect to Bluetooth devices on the whitelist, avoiding the risk of data transfer via Bluetooth at the source. A logistics company used this feature to prevent drivers from transferring delivery route data from their tablets to their personal mobile phones.
3. Port Operation Traceability:
All port enable/disable operations are recorded in the MDM's audit logs. These logs are stored in encrypted format, cannot be manually modified, and can serve as evidence for compliance audits. A cross-border e-commerce company successfully passed a GDPR audit by using these logs to demonstrate that "the company has taken sufficient measures to control physical ports."
Application access control: Prevent unnecessary applications from consuming data resources
Non-work-related apps (such as video apps and social media) are the main drivers of excessive mobile data usage a survey shows that 30% of data consumption on enterprise devices comes from employees using apps like TikTok and Netflix. App access control can reduce unnecessary data usage and lower the risk of malware infection.
1. Application Whitelist Management:
Through MDM (such as AirDroid Business), an "application whitelist" is set up, allowing only essential business software to be installed on devices, such as inventory management systems in the retail industry and electronic health record (EHR) software in the healthcare industry. Downloading video, game, and social media applications is prohibited. If an employee attempts to install an app not on the whitelist, the system will automatically block the installation request and display the message "This application is not authorized by the company and cannot be installed." After adopting this strategy, a chain supermarket reduced its average monthly data consumption per device from 8GB to 3GB, saving 240,000 yuan in communication costs annually.
2. Application Traffic Monitoring and Alerts:
Real-time monitoring of data usage by each application on the device allows setting reasonable thresholds for high-data-consuming business apps (such as map synchronization functions in logistics software). When an application's daily data consumption exceeds a preset value (e.g., 1GB), MDM will send an alert to the IT team to assist in investigating any abnormal usage (such as software automatically downloading update packages in the background). A transportation company used this feature to discover a logistics app was consuming excessive data in the background. They promptly contacted the software vendor to fix the issue, reducing monthly excess data charges by 12,000 yuan.
3. Remote Uninstallation of Unauthorized Apps:
If unauthorized apps are found on devices (such as video software installed by employees through third-party channels), the IT team can remotely uninstall them through the MDM backend without on-site intervention. An educational institution used this feature to clean up unauthorized apps on 200 teaching tablets in just 10 minutes, preventing further data waste.
Best Practice 2: Shifting from a "Reactive Firefighting" to a Mobile device proactive management Model
Traditional mobile data management often operates on a reactive, firefighting basis: investigating data misuse only after receiving excessive bills or tracing the source of data breaches. This model is not only slow and costly but also fails to address the root causes of problems. Effective management must shift to proactive prevention defining risks through pre-emptive policies, identifying risks through real-time monitoring, and automating responses to block risks, thus nipping problems in the bud. This shift highlights the contrast between IT reactive vs proactive management approaches.
Three major pain points of passive management: Why "firefighting" style control is unsustainable
The IT manager of a manufacturing company once lamented, "From the 1st to the 5th of each month, the team is busy checking the previous month's mobile data bills, identifying which devices exceeded the limits, and then contacting employees to confirm the reasons. This task alone takes up 20% of our manpower and time, and often, due to employee turnover and equipment relocation, it's impossible to trace responsibility." This is a typical dilemma of passive management, which can be summarized into three major pain points:
1. High Costs: Double Consumption of Labor and Excessive Expenses
Under passive management, the IT team needs to spend a significant amount of time handling "aftermath": 15-20 hours per month to check excess bills, matching devices and users one by one; after a data breach, it takes 1-2 weeks to trace the source, during which customer compensation and compliance fines may occur. Furthermore, excess data charges resulting from a lack of real-time control are a fixed expense one retail company's 100 POS terminals incurred an average monthly excess data charge of 30,000 yuan, exceeding 360,000 yuan annually, due to employees using their personal mobile phones as hotspots.
2. Slow Response: Missing the Golden Period for Risk Management
The core problem of passive management is its "lag" an investigation is only initiated when problems arise (such as excessive bills or data breaches). A healthcare company experienced an incident where a lost nursing tablet was used to transfer patient medical records via a hotspot. Due to a lack of real-time monitoring, the IT team only discovered the problem three days later through abnormal billing, by which time 50 patient records had already been leaked. The company ultimately paid a $500,000 fine to the HIPAA.
3. Uncontrollable Risks:
Reliance on Employee Self-Discipline Leads to High Violation Rates. Passive management essentially relies on "employees consciously following the rules," but in practice, employees may violate regulations due to "convenience" or "lack of awareness of the risks." A survey showed that 60% of hotspot activations were done to save data on personal mobile phones, not intentionally leaking data. This "unintentional violation" significantly reduces the effectiveness of passive management in preventing risks.
The three pillars of proactive management: proactive policy implementation, real-time monitoring, and automatic response.
The core logic of proactive management is "replacing manpower with rules and remediation with prevention," building a closed loop through three pillars to control risks before they occur:
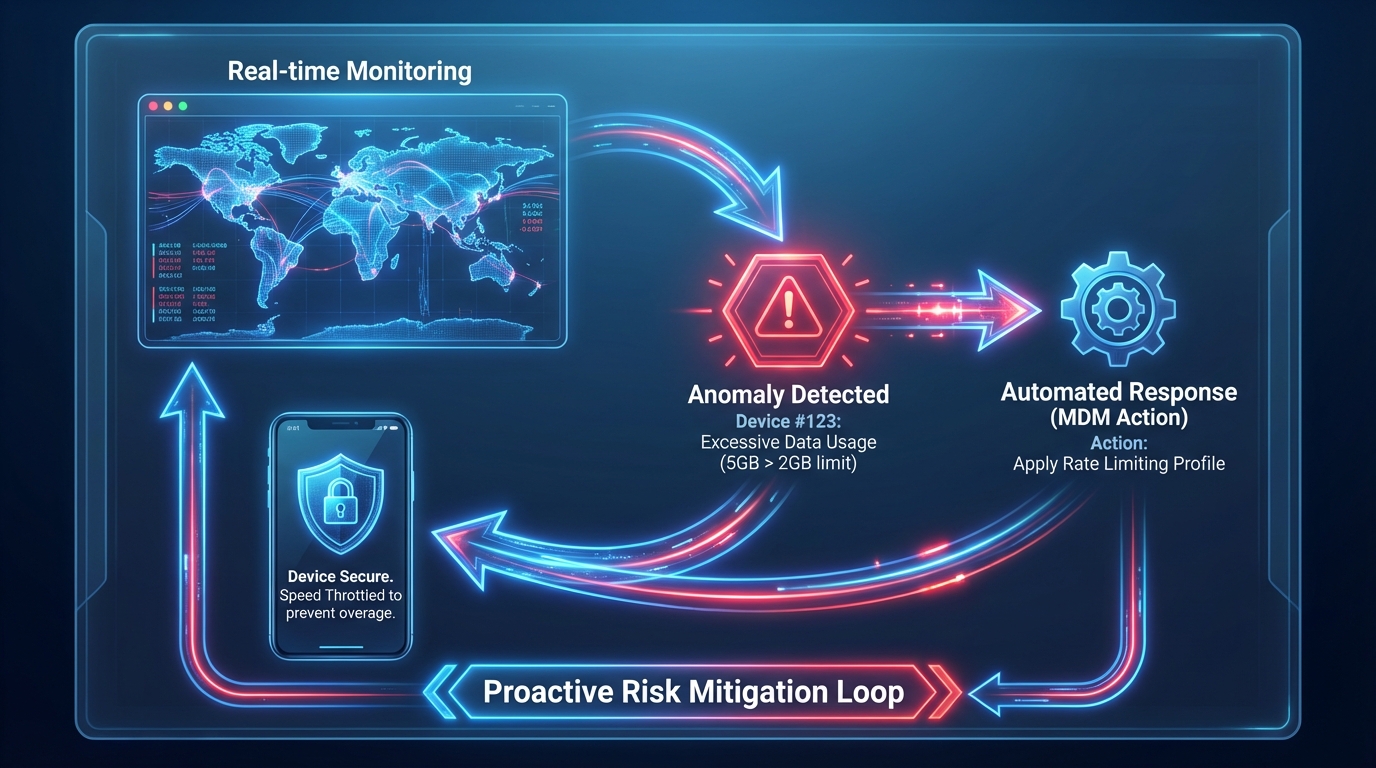
Policy-driven: Embedding risk control into rule design
Policy is the "foundation" of proactive management. It requires developing refined data usage rules based on business scenarios, clearly defining "who can use it, when to use it, and how much to use," and then pushing these policies to all devices using MDM tools to achieve a high rate of policy implementation and execution:
1. Tiered Traffic Limits:
Set differentiated traffic limits based on device usage and employee roles—5GB per month for field tablets (requiring frequent data synchronization), 2GB for office tablets, and 1GB for POS terminals (transmitting transaction data only). A logistics company reduced its average monthly traffic consumption per device from 6GB to 3.2GB through tiered limits, saving 288,000 yuan in annual communication costs.
2. Scenario-Based Function Control:
Pre-set rules for high-risk scenarios, such as "automatically disabling hotspot and USB data transfer functions during non-working hours (18:00 - 8:00 the next day)" and "disabling Bluetooth and application installation permissions after the device leaves the office area (identified by geofencing)." A financial company reduced device violations during non-working hours by 90% after adopting this strategy.
3. Batch Policy Deployment:
Utilize the "Device Grouping" function of MDM (such as AirDroid Business) to categorize devices by department and purpose (e.g., "Retail Store POS Group" and "Field Logistics Tablet Group"). Push corresponding management policies to different groups to avoid a "one-size-fits-all" approach. For example, grant temporary hotspot application permissions to the "Field Logistics Tablet Group" while permanently disabling hotspots for the "Retail Store POS Group," thus meeting business needs while controlling risks.
Real-time monitoring: Dynamically track data usage status
Real-time monitoring is the "eye" of proactive management—through MDM dashboards, IT teams can monitor the data flow and functional status of all devices at any time, and promptly detect abnormal behavior:
1. Multi-dimensional data dashboards:
MDM (such as AirDroid Business) provides visual dashboards displaying key metrics: total number of devices, online/offline status, top 10 devices using traffic, number of hotspot activations, number of violation alerts, etc. IT teams can quickly understand the overall management situation without logging into each device individually. An IT manager at a company stated, "Data reports that used to take a day to compile can now be viewed in 5 minutes through the dashboard, a huge improvement in efficiency."
2. Multi-threshold alarm mechanism:
Setting tiered alarm thresholds for early risk warnings:
- Traffic alarm: When a device's traffic usage reaches 80% of its limit, a "Traffic Exceeding Limit" alert is sent, allowing the IT team to adjust limits or remind employees to conserve traffic.
- Function alarm: When a device attempts to enable unauthorized functions (such as hotspots or USB data transfer), an "Unauthorized Operation Alarm" is immediately sent, including the device ID, user, and operation time.
- Network alarm: When a device connects to an unauthorized network, a "Network Security Alarm" is sent, assisting the IT team in rapid intervention.
3. Geographically correlated monitoring:
Link device location with data behavior. For example, "A field tablet consumes 3GB/day of data in city A (without enterprise Wi-Fi coverage) but only 0.5GB/day in city B (with enterprise Wi-Fi coverage)". The IT team can use this information to optimize network deployment (such as increasing Wi-Fi coverage in city A) and further reduce data costs.
Automated response: Reduces human intervention and improves handling efficiency
Automated response acts as the "hands and feet" of proactive management—for abnormal behaviors detected by monitoring, MDM automatically triggers actions to minimize manual intervention and significantly shorten risk handling time:
1. Automatic Rate Limiting for Excess Traffic:
Some advanced MDM tools support automatically switching the device network to a rate-limiting mode when the device's traffic exceeds its limit. A retail company used this feature to avoid POS terminal network outages caused by excessive traffic.
2. Automatic Blocking of Unauthorized Operations:
When a device attempts to open an unauthorized hotspot, the system automatically disables the hotspot function and displays a pop-up message to employees stating, "This operation is not authorized. Please contact the IT team for permission to use it," while simultaneously sending an alert to the IT team. A medical company used this feature to reduce unauthorized hotspot openings from 20 times per month to 1 time.
3. Automatic Generation of Management Reports:
Weekly/monthly mobile data management reports are automatically generated, including "traffic usage summary, statistics of unauthorized operations, and cost-saving analysis," eliminating the need for manual compilation by the IT team. These reports can be directly used for management presentations, helping decision-makers intuitively understand the management effectiveness of MDM.
Proactive Device Management with AirDroid Business
Move beyond reactive management with AirDroid Business. Implement automated monitoring and response to prevent risks and improve efficiency across your enterprise.
Best Practice 3: Prove the Value of Mobile Data Management with Quantitative ROI
Many companies hesitate when introducing Mobile Data Management (MDM):"How much real value will it bring after the investment?"
In fact, the value of mobile data management is not an "abstract concept," but can be quantified using the formula "risk reduction + cost savings"ROI (MDM ROI calculation) = (Risk reduction benefit + Cost saving benefit) - MDM investment cost. A clear ROI model can not only convince management to approve the budget, but also help companies optimize their management strategies and focus on high-value areas. This quantification plays a critical role in IT risk avoidance value calculation and demonstrates the relevance of Total cost of ownership mobile device management (TCO) analysis.
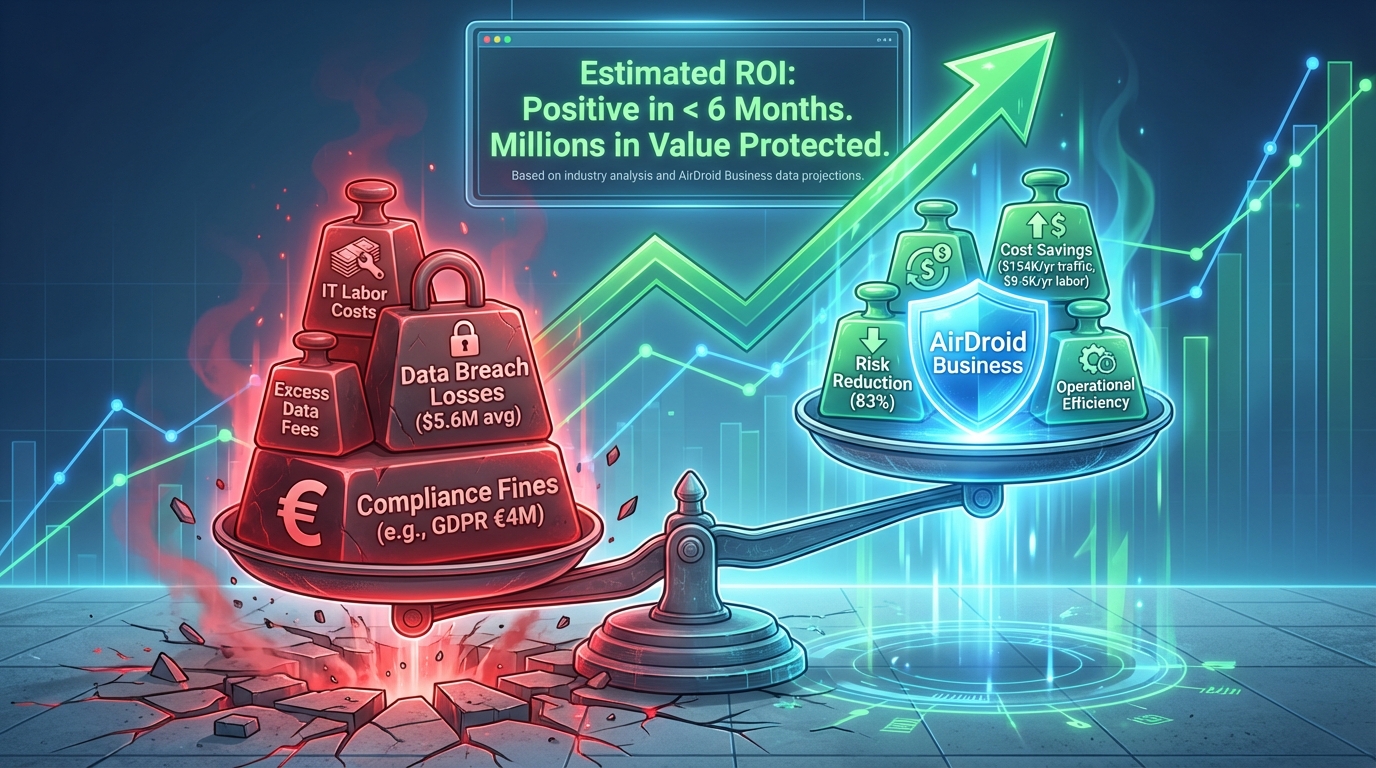
Risk reduction benefits: Avoiding compliance fines and data breach losses
Compliance fines and data breaches represent the "biggest potential costs" of enterprise mobile data management. Globally, GDPR fines for serious violations are capped at 4% of a company's global annual turnover or €20 million (whichever is higher), HIPAA fines are up to $1.5 million per violation, and PCI-DSS fines range from $50 million to $100,000 per month. MDM can directly avoid these losses by blocking the risk of data breaches.
1. Calculation of Avoiding Compliance Penalties
Formula: Avoided Compliance Penalties = Potential Penalty Amount × Risk Reduction PercentageExample: A cross-border e-commerce company with annual revenue of €100 million could face a maximum fine of €4 million if it violates GDPR due to a mobile data breach. Before implementing
AirDroid Business, the probability of a data breach was approximately 30%. After implementation, through hotspot control, port restrictions, and log auditing, the risk was reduced to 5%, a reduction of 83% (30% - 5%). Therefore, the avoided compliance penalty amount = €4 million × 83% = €3.32 million, far exceeding the annual MDM investment of €100,000.
2. Calculation of Avoiding Data Breach Losses
Data breach losses include customer compensation, brand restoration, and business interruption costs. IBM's "2024 Cost of Data Breach Report" shows that the average loss for a single data breach for a global enterprise is $5.6 million.
Case Study:
A healthcare company has 1,000 nursing tablets. If one tablet leaks 100 patient records, the company would need to pay $1,000 in compensation to each patient, resulting in a single leak costing $100,000. After implementing AirDroid Business, through USB disabling and hotspot management, the risk of data leakage was reduced from 25% to 0. This prevents 2.5 potential leaks per year (1,000 tablets × 25% risk × 0.01 leaks/tablet), resulting in a loss avoidance of $2.5 × $100,000 = $250,000.
Cost savings benefits: Reduced excess expenses and IT manpower consumption
Excess traffic fees and IT personnel costs are "fixed expenses" for enterprise mobile data management. MDM can significantly reduce these two costs through real-time control and automation:
1. Calculation of Excess Traffic Fee Savings
Formula: Annual Excess Traffic Fee Savings = Number of Devices × Average Monthly Excess Fee per Device × 12 Months × Reduction Percentage
Example: A retail company has 500 POS terminals. Before implementing MDM, the average monthly excess traffic fee per device was $30, with an excess rate of 35%. After implementing AirDroid Business, through traffic limits and application control, the excess rate dropped to 5%, a reduction of 86% (35% - 5%). Therefore, the annual excess traffic fee saving = 500 devices × $30 × 12 months × 86% = $154,800.
2. IT Labor Cost Savings Calculation
Formula: Annual IT Labor Cost Savings = Average Monthly Labor Hours × 12 Months × Hourly Wage × Reduction Percentage
Example: A company's IT team needs to spend 20 hours per month checking mobile data bills and handling violations. IT staff earn $50 per hour, and labor costs account for 80% of total costs (the remaining 20% is essential work). After introducing AirDroid Business, automated reporting and alerting functions reduce labor time by 80%, a reduction of 80%. Therefore, the annual IT labor cost savings = 20 hours × 12 months × $50 × 80% = $9600.
Simplified ROI calculation template (can be used directly)
To help businesses quickly estimate the ROI of MDM, the following template can be used directly, with an example based on actual data from a medium-sized retail company (100 devices):
Calculation Dimension | Company Baseline Data | Improvements Brought by MDM | Annual Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Risk Reduction Gains | Potential GDPR fine of €4 million, with a risk probability of 30% | Risk reduced to 5% (an 83% reduction) | €3.32 million |
| Excess Data Usage Savings | 100 devices, each exceeding data usage by an average of $30 per month | Excess usage rate reduced from 35% to 5% (an 86% reduction) | $154,800 |
| IT Labor Savings | Average monthly labor of 20 hours, hourly wage $50 | Time reduced by 80% | $9,600 |
| Annual MDM Investment | - | - | $12,000 |
| Net ROI | - | - | €3.32 million + $152,400 |
As the examples show, the return on investment for MDM primarily comes from "risk reduction" (especially avoiding compliance penalties), while cost savings are an "additional benefit." For regulated industries (healthcare, finance, retail) or companies with large-scale equipment, the ROI cycle for MDM can typically be shortened to 3-6 months.
Best Practice 4: Differentiated Implementation Strategies Based on Industry Characteristics
Mobile data management needs vary significantly across different industries: the healthcare industry prioritizes patient data privacy (compliant with HIPAA), the retail industry focuses on payment data security (compliant with PCI-DSS), and the logistics industry needs to balance remote data needs with cost control. Therefore, best practices must be implemented "tailored to local conditions," with differentiated strategies designed based on industry characteristics.

Retail Industry: Focusing on Payment Data Security and Traffic Cost Control
The core mobile devices for retail enterprises are POS terminals and inventory management tablets. Data management needs to address two major issues: first, preventing POS terminals from leaking customer payment information (compliant with PCI-DSS); and second, preventing inventory management tablets from generating excessive data traffic due to employee misuse.
1. POS Terminal: Full Function Lock + Log Audit:
- Permanently disable the hotspot and USB data transfer functions of the POS terminal, retaining only the "charging + enterprise Wi-Fi connection" function to prevent payment data from being copied via hotspot or USB;
- Set a data limit (1GB per terminal per month), automatically throttling the speed after exceeding the limit to avoid data waste caused by employees installing video software without authorization. After a chain supermarket adopted this strategy, the excess data fee for the POS terminal dropped from 20,000 yuan per month to 0, and the PCI-DSS audit passed on the first attempt.
2. Inventory Management Tablet: Dynamic Limits + Scenario Authorization
- Set dynamic traffic limits based on peak and off-peak seasons: 3GB/month during peak season and 1.5GB/month during off-peak season to avoid resource waste.
- Allow the inventory tablet to request temporary hotspot access (maximum 1 hour) when there is no Wi-Fi in the store for synchronizing inventory data. Access is automatically deactivated upon expiration, and the IT team can track usage records through logs.
Healthcare industry: Compliant with HIPAA, protecting patient data privacy
Mobile devices in the healthcare industry (nursing tablets, monitors, doctors' ward round tablets) store a large number of patients' electronic medical records (EHRs). Data management must strictly comply with HIPAA requirements: all data transmission must be encrypted and traceable, and transmission through unauthorized channels (such as hotspots, USB) is prohibited.
1. Nursing Tablet: Port Disabling + Temporary Authorization
Disable the USB port and Bluetooth function of the nursing tablet, allowing only encrypted VPN connections to the hospital intranet to ensure secure transmission of EHR data only within the hospital;
Integrate with the hospital's existing OA system to grant temporary hotspot access only to attending physicians, with time limits set (e.g., a maximum of 2 hours), for synchronizing patient data during emergency consultations. Usage records are synchronized to the HIPAA audit log in real time;
Retain 7 years of data usage logs for the nursing tablet (as required by HIPAA), including "who used it, when data was transmitted, and the type of content transmitted," which can be exported at any time for audit verification. One hospital achieved zero violations in HIPAA audits for three consecutive years using this strategy.
2. Patient Monitor: Network Lockout + Anomaly Alarm:
Restrict the patient monitor to connect only to the hospital's dedicated Internet of Things (IoT) network, prohibiting connection to public Wi-Fi or hotspots to prevent leakage of real-time vital signs data;
Set up "Data Transmission Anomaly Alarm": If the amount of data transmitted per unit time by the patient monitor shows abnormal fluctuations, the system can automatically identify and immediately send an alarm to the IT team and the head nurse of the department.
Logistics Industry: Balancing Remote Data Needs and Cost Control
The core mobile device in the logistics industry is the tracking tablet of field drivers, which needs to frequently synchronize route information, delivery records, and fuel consumption data. Data management needs to resolve the contradiction between "network requirements in remote scenarios" and "traffic cost control".
1. Geofencing + Dynamic Network Policies:
Through advanced geofencing capabilities, MDM tools can implement dynamic network policies: for example, when the tablet enters a specific area with enterprise Wi-Fi, it can be configured to automatically disable the hotspot and switch to Wi-Fi; when the tablet leaves the area and enters a remote route, it can be allowed to automatically enable the hotspot according to the policy (only for synchronizing specific business data), and a traffic limit can be set;
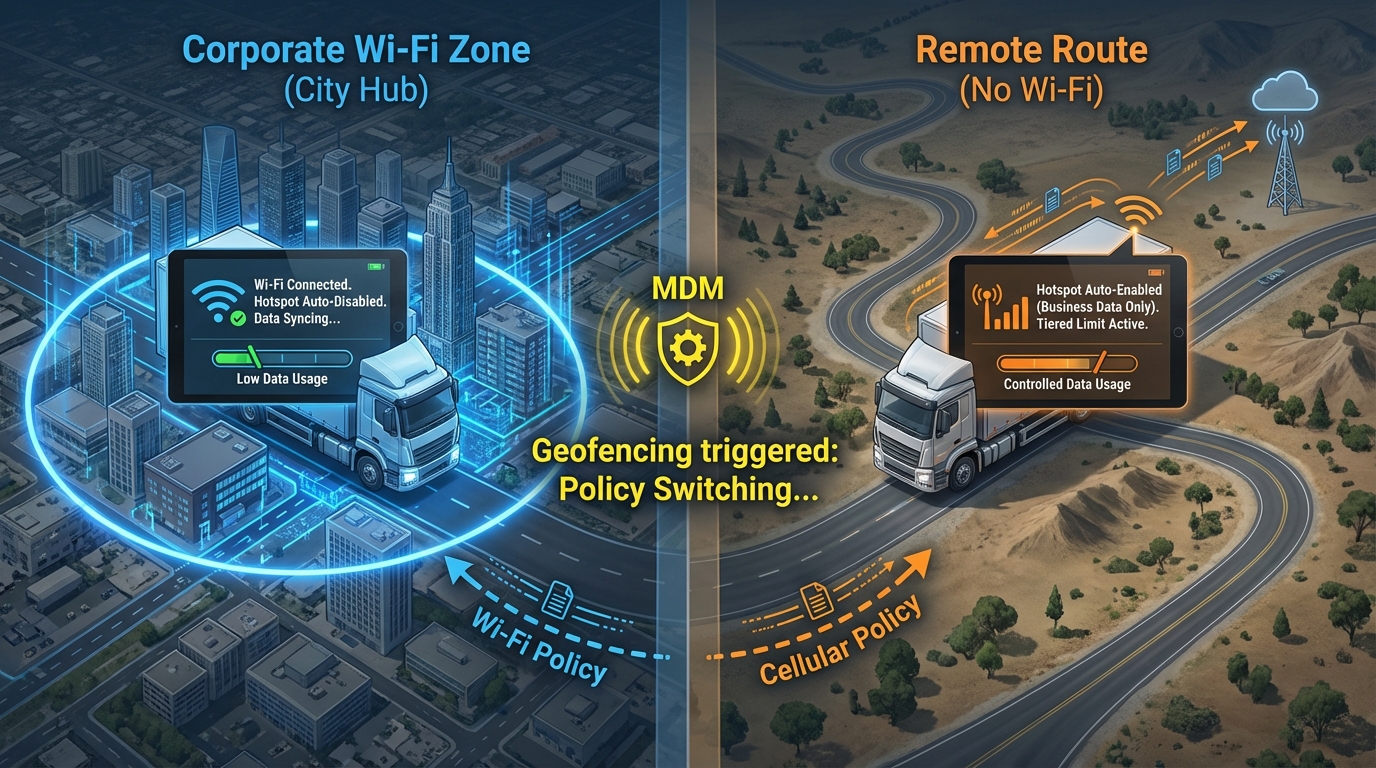
Enabling "Offline Mode" for the Logistics Management App: When the tablet is in an area without network access, it automatically caches delivery records and route information, and synchronizes them in batches when it enters an area with network access, reducing the traffic consumption for real-time data transmission. After adopting this strategy, a logistics company reduced the average monthly traffic consumption of its field tablets from 8GB to 4.5GB, saving 216,000 yuan in communication costs annually.
2. Driver Behavior Control + Cost Allocation
Record the usage of logistics tablets. If drivers are found to be frequently using video or game apps, send reminders and notify fleet management to reduce non-work-related data consumption; Allocate data costs according to the length of the transportation route (e.g., 5GB limit for long-distance routes and 2GB limit for short-distance routes) to match cost control with business needs.
Secure Your Enterprise with AirDroid Business
Establish a scientific mobile data management model with AirDroid Business. Achieve the optimal balance between security and efficiency, transforming mobile data into a business growth driver.
Conclusion
MDM is the "infrastructure" for enterprise mobile data management.
In today's digital transformation, mobile devices have become the "core carrier" of enterprise operations from retail store checkouts to hospital ward rounds, from logistics vehicle tracking to field staff operations, almost all key processes rely on the support of mobile data. Therefore, mobile data management is no longer a "minor matter for the IT department," but a "strategic matter" related to enterprise security, cost, and compliance.
The five best practices proposed in this article building a comprehensive access control framework, shifting to proactive preventative management, quantifying the ROI value of MDM, tailoring implementation to industry characteristics, and strengthening employee collaboration are essentially a complete system "from risk prevention to value creation." MDM solutions such as AirDroid Business serve as the "infrastructure" for implementing this system: they translate abstract policies into concrete actions on the device side, achieving "no blind spots in control"; they enable "risk prevention" through real-time monitoring and automated response; and they allow "value quantification" through logs and reports.
For businesses, adopting MDM is not just about "buying a tool," but about "establishing a scientific mobile data management model" it helps them find the optimal balance between "security" and "efficiency," mitigating the risk of data breaches, avoiding excessive costs, and ensuring uninterrupted employee work, ultimately transforming mobile data from a "source of risk" into a "booster for business growth." In the future, with increasingly stringent data compliance requirements and a continuously expanding scale of devices, MDM will become an indispensable part of enterprise digital transformation.







Leave a Reply.