AirDroid Business vs. Intune: A Deep Comparison of Enforced Access Control, Identity Authorization, and Android Professional Features
This article aims to provide an in-depth comparison of AirDroid Business, a professional mobile device management (MDM) solution focused on the Android platform, and Microsoft Intune, a universal unified endpoint management (UEM) platform, across key enterprise security and operational metrics.
The analysis reveals that in areas involving deep policy control over a fleet of dedicated Android devices, particularly data leak prevention (DLP) and real-time permission management, AirDroid Business's specialized architecture offers a higher level of mandatory policy enforcement and greater authorization efficiency.
As a general-purpose UEM, Intune's policy enforcement primarily relies on configuration and application programming interface (API) calls, which may leave potential risks of bypass at the system's underlying level.
In contrast, AirDroid Business employs a system-level mandatory access control (MAC) mechanism designed to achieve unbypassable policy locking, crucial for enterprises adhering to stringent compliance standards.
Compliance reports show that up to 40% of compliance penalties are related to uncontrolled device network behavior (such as hotspot abuse); AirDroid Business's mandatory policies are a core countermeasure against such risks.
In terms of operational efficiency, Intune's policy synchronization cycle, especially on Android devices, can be as long as approximately 8 hours, with additional latency when relying on Azure AD dynamic grouping.
AirDroid Business's instant loading of policies and vertically integrated identity authorization capabilities are key to ensuring that dynamic role changes take effect in real time, thereby eliminating long security windows and providing IT teams with lower operational friction.
Android device policy mandates compliance background

The Positioning and Boundaries of General-Purpose UEM and Professional-Purpose MDM
General-purpose UEM platforms, such as Microsoft Intune, are designed with the core principle of providing unified management across all major endpoint operating systems, including Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, and ChromeOS. This multi-OS support provides enterprises with a centralized point of control, but often at the cost of sacrificing deep control over specific platforms, especially the Android ecosystem.
In contrast, specialized MDM solutions, such as AirDroid Business, focus their resources and development efforts on the Android platform, aiming to provide in-depth enterprise-level management, monitoring, and security capabilities.
Their feature sets are highly focused on scenarios specific to Android devices, such as powerful Kiosk mode, remote control, unattended device management, and system-level deep security policy enforcement. This specialized positioning enables them to handle low-level system control needs that are difficult for general-purpose UEMs to address.
DLP Challenges in a Regulatory Environment: Risk Models of Hotspot Sharing and Unencrypted Data Transmission
The current global data regulatory environment is becoming increasingly stringent (such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS), and the requirements for corporate compliance have shifted from abstract "document-level formalism" to "device-level actual implementation." Regulatory requirements translate abstract principles into controllable and traceable data transmission mechanisms, making mandatory access control (MAC) and identity-based access control crucial.
Hotspot sharing has become a major area of compliance risk on enterprise-specific Android devices. Employees enabling hotspot sharing without authorization allows non-enterprise-certified personal devices to connect to the company intranet, bypassing mandatory VPN policies.
This can lead to the transmission of sensitive data (such as customer privacy data, medical records, or payment information) through unencrypted or uncontrolled channels, making them highly vulnerable to interception or theft and directly triggering regulatory penalties.
A professional MDM solution must be able to translate the abstract regulatory principle of "ensuring data controllability" into an unavoidable, enforceable policy on the device side, thereby achieving a closed loop of "regulatory requirements > IT policies > device behavior," which is a decisive factor for successful compliance audits.
A Battle of Execution Force: MAC vs. Configuration Management
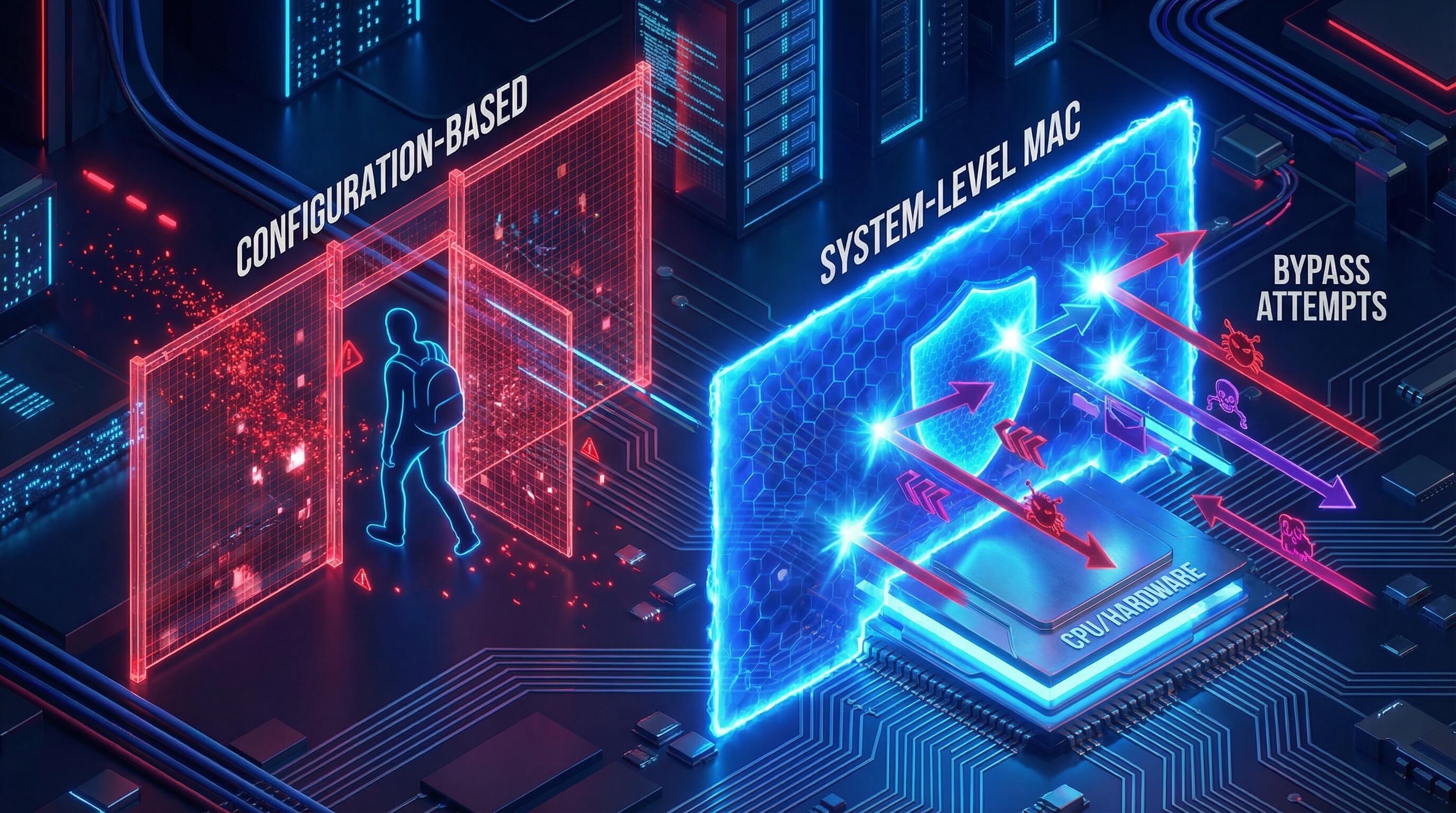
In terms of security policy enforcement, the technical differences between mandatory and configurable approaches determine an enterprise's risk exposure when faced with insider bypassing or accidental misconfiguration.
Policy execution depth: System-level MAC (Mandatory Access Control)
AirDroid Business's Mandatory Mechanism: An Analysis of Unbypassable System-Level Policy Lock-in
AirDroid Business's core strength lies in the enforceability of its policies [Query 1.1.1]. Its execution mechanism is designed for system-wide, unavoidable enforcement, continuously locking down critical functionalities such as Hotspot.
The goal is to eliminate the flexibility technical staff might attempt to manipulate policy settings, ensuring absolute policy execution. This design enables enterprises to achieve the "traceable use" requirement in compliance audits.
This deep, system-level execution indicates that AirDroid Business employs a management interface that goes beyond the limitations of the standard Android Enterprise API.
Technically, this suggests that its MDM Agent may utilize mechanisms at a lower level than ordinary configuration management, similar to dynamic memory instrumentation, thereby possessing absolute control over resource access at the core system functionalities level, such as network sharing.
In highly compliant or dedicated device environments, the "mandatory" rather than "tolerant" nature of policies is indispensable. AirDroid Business's MAC policy provides a zero-tolerance security boundary, preventing any unauthorized data outflow.
Limitations and configurability of Intune: Configuration risks associated with relying on OEMConfig
As a general-purpose UEM, Microsoft Intune primarily provides configuration management services through the Android Enterprise interface. For deep control over the system's underlying layers or specific brands, Intune often relies on Google's standardized OEMConfig mechanism.
OEMConfig allows original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) to write applications with configuration schemas and distribute them through Google Play to extend Intune's native feature set.
While the OEMConfig pattern offers flexibility, it introduces inherent complexity and reliability limitations. IT administrators must process complex JSON templates provided by the OEM within Intune to configure settings, increasing configuration complexity.
More importantly, functionality and reliability are constrained by vendor differences, and the maximum size of each OEMConfig configuration file is limited to 500 KB, posing a challenge for large-scale, fine-grained policy deployment.
Intune must serve all platforms, therefore its architecture prevents it from embedding overly customized, deeply controlled logic within the Android system kernel, thus compromising policy uniformity and reliability.
Get Security That Can’t Be Bypassed
Don't leave your compliance to chance. While general UEMs rely on flexible APIs, AirDroid Business uses system-level Mandatory Access Control to permanently lock hotspots and ports—ensuring your policies are actually enforced, not just suggested.
The breadth and uniformity of port control: A comparison of governance for Hotspot, USB tethering, and Bluetooth.

Unified Port Management Advantages: AirDroid Business's One-Stop Centralized Control
AirDroid Business's expertise is evident in its ability to manage all critical data transfer ports in a single, professional interface. This includes centralized control over features such as Hotspot, USB sharing, and Bluetooth.
This one-stop management is crucial for deploying a comprehensive data loss prevention (DLP) strategy. A DLP strategy must cover all possible data egress vectors, including preventing employees from transferring corporate data to personal devices or external storage via USB.
By managing all transmission ports through a single control point, IT administrators can effectively avoid oversights when configuring multiple policy objects, ensuring that all potential data leakage risks are uniformly and completely covered by mandatory policies.
The fragmentation challenge of UEM: Intune's decentralization and management overhead
Intune's generic UEM architecture presents fragmentation challenges in port control. Achieving unified management of all data-sharing ports may require IT administrators to operate across multiple configuration sets or rules [Query 1.2.2].
For example, restrictions on Hotspot or certain deep-share features may be scattered across different "Device Restrictions" profiles, while certain deep USB restrictions may require reliance on OEM-specific Knox policies or other OEMConfig integrations.
This fragmentation of management significantly increases administrative overhead. Every policy adjustment and verification requires the IT team to operate and cross-check multiple independent configuration interfaces, thereby extending configuration deployment time and increasing the risk of missing configuration points.
Comparative Analysis of Port Control Mechanisms
Endpoint Control Mechanism Comparison Analysis
Control Target | AirDroid Business (Professional MDM) | Microsoft Intune (General UEM) | Execution Depth Difference | Key Compliance Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hotspot / Network Sharing | System-level MAC, policy enforcement, continuous lock¹ | Configuration management, relies on Android API/OEMConfig, potential bypass risks² | Strong enforcement, cannot be bypassed | Hotspot misuse leading to VPN bypass and data leakage |
| USB File Transfer / Sharing | System-level DLP, unified interface control³ | Configuration restrictions, may rely on specific Knox or OEMConfig implementation⁴ | Uniformity and complexity of DLP implementation | Employees exposing corporate data through physical interfaces |
| Policy Deployment Consistency | Unified and dedicated Android console [Query 1.2.1] | Cross-configuration requires reliance on OEM configuration apps⁵ | Level of simplification in deployment and maintenance | Compliance loopholes caused by fragmented configuration |
Comparison of Identity Binding and Authorization Efficiency
The real-time activation of policies is crucial for dynamically managed enterprise environments, such as personnel changes, role switching, or security incident response. AirDroid Business's vertical integration in identity integration and policy synchronization contrasts sharply with Intune's indirect reliance on external cloud services.
Efficiency of binding strategy and user identity: Implementation of efficiency from management to execution.
AirDroid Business's intuitive authorization model: a high degree of integration between the built-in membership system and strategies.
The AirDroid Business platform achieves high integration with policies through its built-in member management system. The platform offers four default roles (Super Admin, Admin, Team Member, Viewer) and supports custom permissions, greatly simplifying the permission allocation process.
IT managers can intuitively and quickly bind policies such as Hotspot permissions to specific user IDs or roles through simple grouping, making the authorization process simple and intuitive [Query 2.1.1].
This vertically integrated model manages identity and policy enforcement on a single professional platform, effectively eliminating the overhead and data mapping required for cross-system switching.
Therefore, AirDroid Business has a significant advantage in the speed of policy formulation, allocation, and implementation, improving policy implementation efficiency.
Integration complexity of Intune: Indirect dependency of the authorization process on Azure AD groups
Intune's authorization model relies on its upstream Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD) for identity and group management. IT administrators must operate across multiple interfaces, first defining user and dynamic device groups in Azure AD, before Intune can assign policies to these groups. This constitutes an indirect dependency model.
This process coupling results in a dual bottleneck affecting the real-time performance of policies:
Firstly, the delay in updating dynamic group memberships in Azure AD (which can take anywhere from minutes to hours), and secondly, the synchronization cycle of the Intune client.
IT teams not only need to manage policies but also continuously monitor and debug the synchronization status between the two systems, making the authorization process relatively indirect and complex. To avoid dynamic grouping delays, Intune recommends assigning policies to user groups with pre-populated members whenever possible.
Impact of Role-Based Dynamic Strategy Loading and Synchronization Delay on Operations

Immediacy of Policy Implementation: AirDroid Business's Advantages in Real-Time Permission Switching
AirDroid Business emphasizes its faster policy loading and switching speeds, ensuring the immediate effect of dynamic policies such as Hotspot permissions [Query 2.2.1].
In scenarios requiring rapid response (e.g., when an employee's role changes necessitate the immediate revocation of data access permissions), the ability to implement policies instantly is a core value of a professional MDM.
This instant response capability is typically achieved through a high-frequency heartbeat mechanism of the local MDM Agent or a proprietary push channel, making it independent of the standard GMS push latency of Android Enterprise. This architecture ensures that devices can execute immediately when IT administrators issue or revoke permissions in the console, thus avoiding any security windows caused by policy delays.
Intune's synchronization dependencies and operational risks: Compliance challenges of Android policy refresh cycles
Intune's policy deployment and reversal rely on cloud synchronization cycles. Maintenance synchronization initiated by Android device clients occurs approximately every 8 hours. Newly registered Android devices, after an initial high-frequency synchronization period, will also revert to a maintenance synchronization cycle of approximately every 8 hours.
This 8-hour window represents a significant operational risk for Intune when dynamic, real-time compliance management is required. In the event of a security incident or urgent role reassignment (e.g., requiring remote erasure or immediate revocation of Hotspot privileges), policy enforcement can be delayed by hours if devices miss push notifications or fail to connect to GMS.
While Intune allows IT administrators to manually trigger device synchronization, this manual intervention-dependent approach is neither scalable nor suitable for compliance scenarios with stringent requirements for dynamic permission switching when managing large fleets of devices. Any delay can translate into compliance vulnerabilities and legal risks.
Comparison of Policy Sync and Dynamic Authorization Efficiency
Don’t Wait 8 Hours to Stop a Breach
Security incidents happen in seconds, not hours. Skip the long sync delays of generic UEMs. AirDroid Business applies policy changes and permission revocations instantly, giving you real-time control when it matters most.
Android Expertise and Operational Efficiency
The difference in platform depth between professional MDM and general UEM directly determines the daily operational efficiency and cost of IT teams when managing a large number of dedicated Android devices.
Professionalization and Intuitiveness of UI Operation
AirDroid Business's professional UI: Optimizing Android management processes and reducing the learning curve.
AirDroid Business's interface is specifically designed for Android device management processes. Policy configuration and device status monitoring are designed to be intuitive and quick, significantly reducing the learning curve for IT teams. User feedback highlights the operational efficiency improvements brought about by this professional UI, with its ease of use and high rating (4.9/5 stars).
For large-scale deployments and routine maintenance, a professional UI/UX enables IT teams to quickly locate Android's unique deep functionalities (such as Kiosk locking and batch APK deployment), reducing configuration errors. This optimization directly shortens daily operation time and is a key factor in reducing the IT department's daily management overhead (OpEx).
Intune's limitations: the complexity and user experience cost of locating specific Android deep configuration entry points.
Intune's interface is a universal UEM designed for all endpoints (Windows, iOS, Android). This universality forces the system to seek a balance in UI design, resulting in the deep configuration entry points specific to the Android platform often being buried in complex menu hierarchies. For example, for OEMConfig that requires deep customization, administrators may need to edit complex JSON templates to implement the configuration.
This configuration friction generates significant hidden costs: IT administrators need to invest more time learning, navigating, and maintaining complex configuration sets.
Historically, Android operating system version upgrades (such as changes in password complexity requirements in Android 11) have led to large-scale policy conflicts, forcing IT administrators to manually adjust complex, Android-specific policies within the generic UEM interface, resulting in device non-compliance incidents. Customized interfaces from professional MDMs typically offer more direct and specialized solutions for dealing with such platform-specific changes.
Remote troubleshooting and in-depth support for Kiosk mode: Ensuring critical business continuity

AirDroid Business's comprehensive support tools include: seamless remote control, black screen mode, and file transfer in Kiosk mode.
AirDroid Business offers industry-leading remote management and troubleshooting capabilities. Its feature set includes powerful remote control, remote file transfer, one-click screenshot/screen recording, and more, making it particularly beneficial for efficient troubleshooting and on-site diagnostics in the IT and Information Security (IT&IS) industry.
For critical dedicated devices such as kiosks and digital signage, AirDroid Business offers unique features to ensure business continuity:
- Seamless file transfer in kiosk mode: Even when devices are locked into single-application or multi-application kiosk mode, administrators can still use remote file transfer to quickly push new media assets or update application files, ensuring timely content and system updates.
- Black Screen Mode: This unique feature allows technicians to turn off the device screen when remotely maintaining unattended devices, thus hiding the remote operation process and ensuring data privacy and security during maintenance.
AirDroid Business's native, deeply integrated toolset significantly reduces Mean Time To Recovery (MTTR), decreases enterprises' reliance on physical field support, and ensures the continuity of critical business operations.
Intune's limitations in deep operation: the necessity of relying on additional licenses or external third-party tools
Intune's native functionality allows for configuration of a basic Kiosk mode, supporting single-application and multi-application locking. However, for complex, high-frequency remote operation and maintenance scenarios, as well as advanced functionalities, Intune's native toolset has limitations [Query 3.2.2].
If businesses require the seamless, in-depth remote control experience offered by AirDroid Business, they typically need to purchase additional add-ons. Intune's Remote Help feature is a paid cloud service with hefty licensing fees (e.g., $3.50/user/month) and requires licensing for the entire Intune tenant.
This means that to obtain in-depth remote support capabilities comparable to a professional MDM, businesses will inevitably increase their Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) and may need to integrate third-party solutions such as Splashtop or TeamViewer, introducing additional integration and management complexity.
In-depth Android Operations and Troubleshooting Function Matrix
Feature | AirDroid Business | Microsoft Intune (Native / Add-on) | Impact on Kiosk Mode Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unattended Remote Control | Highly optimized, fast, low latency | Limited; requires purchasing the expensive Remote Help add-on license | Significantly reduces onsite support costs and enables remote self-healing |
| Remote File Transfer (Kiosk) | Seamlessly integrated, works even in lock mode | Usually requires complicated steps or reliance on third-party apps | Quickly update content or push diagnostic files to keep devices running in real time |
| Remote Operations Privacy Protection | Built-in Black Screen Mode | Lacks native support | Ensures privacy and security compliance during remote operations |
| Interface Optimization Level | Purpose-built for Android MDM with professionalized management workflows | General UEM interface with long configuration paths | Improves daily IT operation speed and accuracy |
Stop Paying Extra for Remote Support
Why pay additional licensing fees for basic remote tools? AirDroid Business includes advanced remote control, black screen mode, and file transfer natively—lowering your TCO while speeding up your troubleshooting.
Conclusion
Professional MDM is the best choice for mandatory compliance and operational efficiency.

Final Recommendation: For enterprises that use Android devices as core business operation tools (such as retail, logistics, and dedicated information terminals) and have the highest requirements for data transmission compliance, policy enforcement depth, and real-time operational efficiency, choosing AirDroid Business as a professional Android MDM solution is the best strategy to achieve mandatory compliance and operational excellence.
In a multi-platform environment, it can serve as a crucial and in-depth supplement to general UEMs (such as Intune), focusing on the management of high-risk, high-value Android assets.







Leave a Reply.